- Calcium & bone metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database)
- Increased Risk of Hip Fracture in Patients with Acromegaly: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea
-
Jiwon Kim, Namki Hong, Jimi Choi, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Sin Gon Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):690-700. Published online October 30, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1782
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
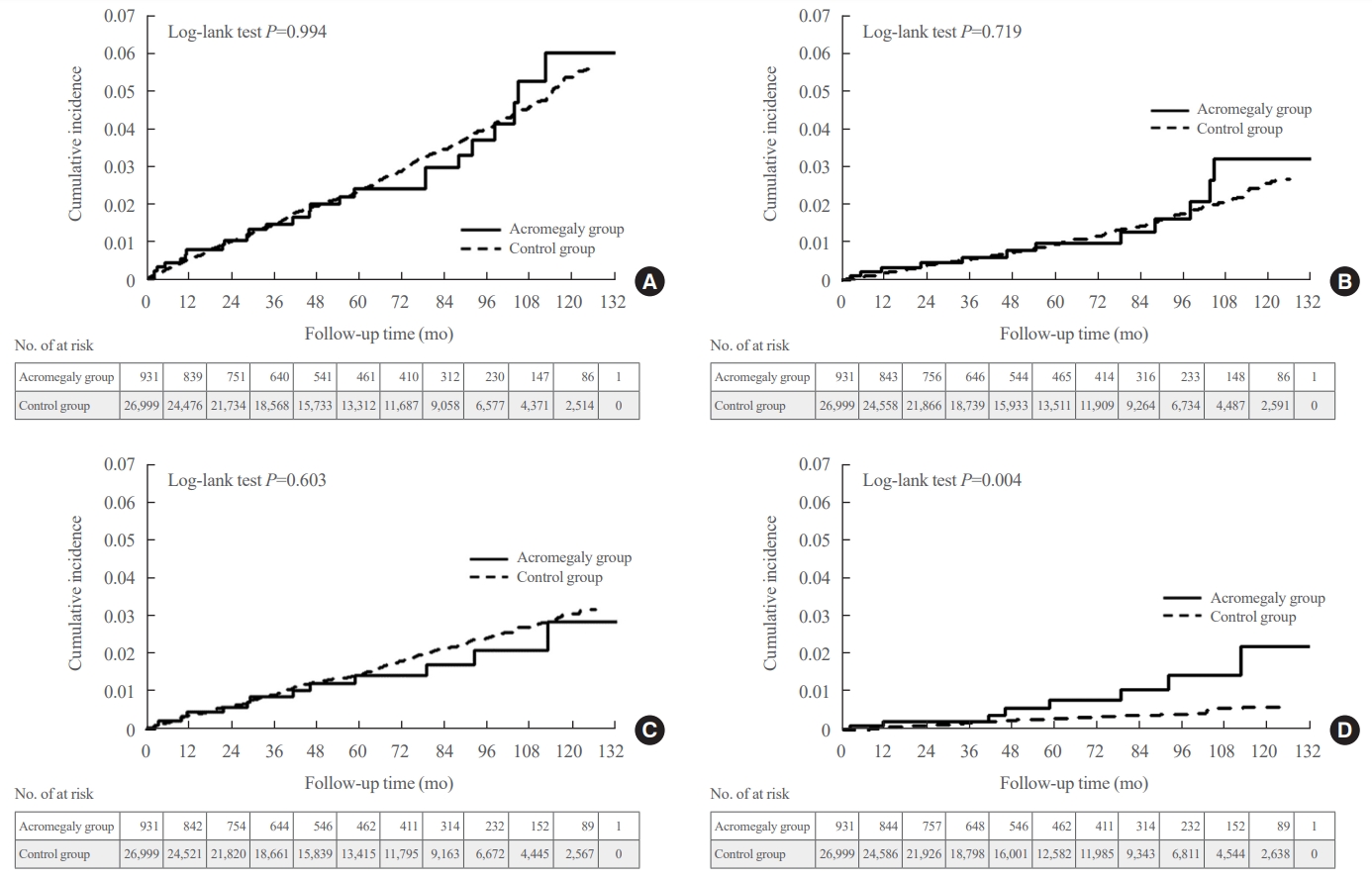
Acromegaly leads to various skeletal complications, and fragility fractures are emerging as a new concern in patients with acromegaly. Therefore, this study investigated the risk of fractures in Korean patients with acromegaly.
Methods
We used the Korean nationwide claims database from 2009 to 2019. A total of 931 patients with acromegaly who had never used an osteoporosis drug before and were treated with surgery alone were selected as study participants, and a 1:29 ratio of 26,999 age- and sex-matched osteoporosis drug-naïve controls without acromegaly were randomly selected from the database.
Results
The mean age was 46.2 years, and 50.0% were male. During a median follow-up of 54.1 months, there was no difference in the risks of all, vertebral, and non-vertebral fractures between the acromegaly and control groups. However, hip fracture risk was significantly higher (hazard ratio [HR], 2.73; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.32 to 5.65), and non-hip and non-vertebral fractures risk was significantly lower (HR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.17 to 0.98) in patients with acromegaly than in controls; these results remained robust even after adjustment for socioeconomic status and baseline comorbidities. Age, type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardio-cerebrovascular disease, fracture history, recent use of acid-suppressant medication, psychotropic medication, and opioids were risk factors for all fractures in patients with acromegaly (all P<0.05).
Conclusion
Compared with controls, patients surgically treated for acromegaly had a higher risk of hip fractures. The risk factors for fracture in patients with acromegaly were consistent with widely accepted risk factors in the general population.
- Hypothalamus and pituitary gland
- Multiomics Approach to Acromegaly: Unveiling Translational Insights for Precision Medicine
-
Kyungwon Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):463-471. Published online October 13, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1820
-
-
1,728
View
-
122
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
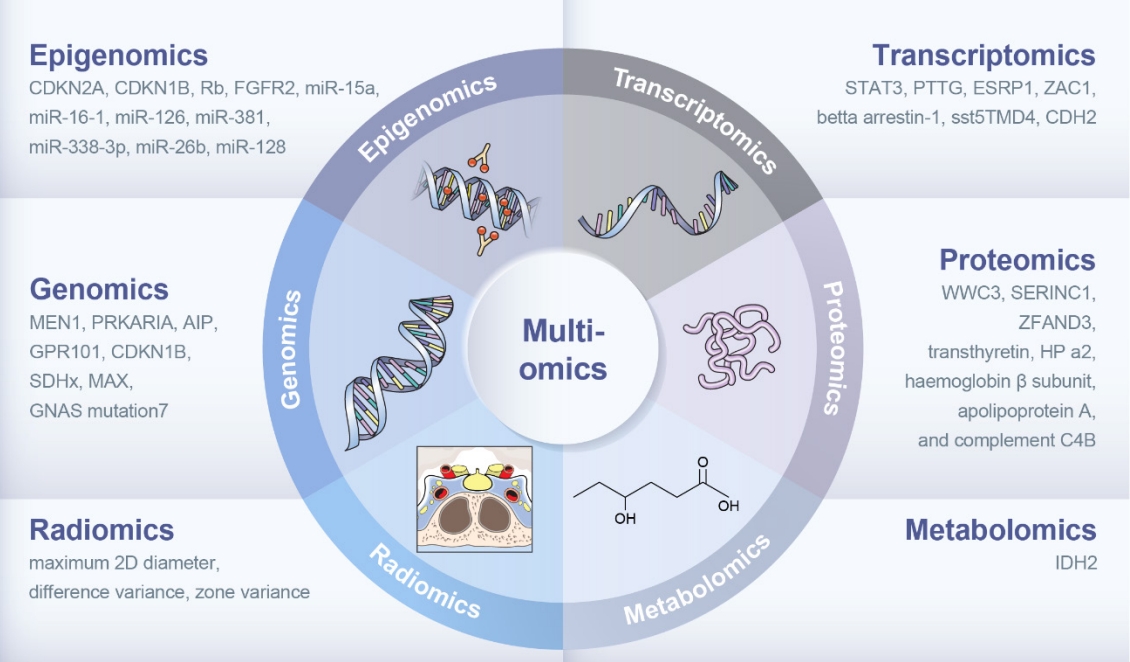
- The clinical characteristics and prognoses of acromegaly vary among patients. Assessment of current and novel predictors can lead to multilevel categorization of patients, allowing integration into new clinical guidelines and a reduction in the increased morbidity and mortality associated with acromegaly. Despite advances in the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly, its pathophysiology remains unclear. Recent advancements in multiomics technologies, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and radiomics, have offered new opportunities to unravel the complex pathophysiology of acromegaly. This review comprehensively explores the emerging role of multiomics approaches in elucidating the molecular landscape of acromegaly. We discuss the potential implications of multiomics data integration in the development of novel diagnostic tools, identification of therapeutic targets, and the prospects of precision medicine in acromegaly management. By integrating diverse omics datasets, these approaches can provide valuable insights into disease mechanisms, facilitate the identification of diagnostic biomarkers, and identify potential therapeutic targets for precision medicine in the management of acromegaly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - “Micromegaly”: Acromegaly with apparently normal GH, an entity on its own?
Lucio Vilar, Luciana Ansaneli Naves, Manoel Ricardo Alves Martins, Antônio Ribeiro-Oliveira Jr
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; : 101878. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Associations of GNAS Mutations with Surgical Outcomes in Patients with Growth Hormone-Secreting Pituitary Adenoma
-
Hyein Jung, Kyungwon Kim, Daham Kim, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Se Hoon Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):342-350. Published online March 23, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.875
-
-
4,351
View
-
143
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
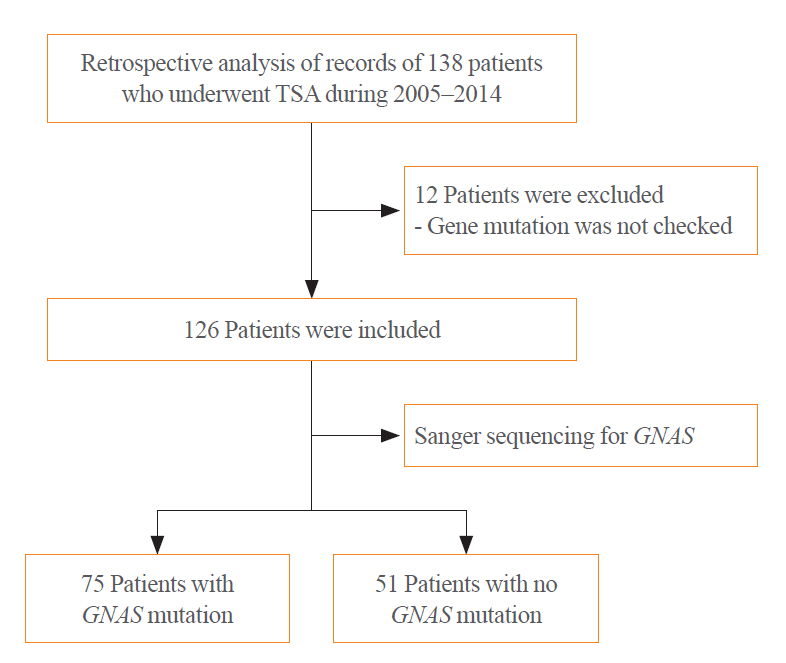
The guanine nucleotide-binding protein, alpha stimulating (GNAS) gene has been associated with growth hormone (GH)-secreting pituitary adenoma. We investigated the prevalence of GNAS mutations in Korean patients with acromegaly and assessed whether mutation status correlated with biochemical or clinical characteristics.
Methods
We studied 126 patients with acromegaly who underwent surgery between 2005 and 2014 at Severance Hospital. We performed GNAS gene analysis and evaluated age, sex, hormone levels, postoperative biochemical remission, and immunohistochemical staining results of the tumor.
Results
GNAS mutations were present in 75 patients (59.5%). Patients with and without GNAS mutations showed similar age distribution and Knosp classification. The proportion of female patients was 76.5% and 48.0% in the GNAS-negative and GNAS-mutation groups, respectively (P=0.006). In immunohistochemical staining, the GNAS-mutation group showed higher GH expression in pituitary tumor tissues than the mutation-negative group (98.7% vs. 92.2%, P=0.015). Patients with GNAS mutations had higher preoperative insulin-like growth factor-1 levels (791.3 ng/mL vs. 697.0 ng/mL, P=0.045) and lower immediate postoperative basal (0.9 ng/mL vs. 1.0 ng/mL, P=0.191) and nadir GH levels (0.3 ng/mL vs. 0.6 ng/mL, P=0.012) in oral glucose tolerance tests. Finally, the GNAS-mutation group showed significantly higher surgical remission rates than the mutation-negative group, both at 1 week and 6 months after surgical resection (70.7% vs. 54.9%, P=0.011; 85.3% vs. 82.4%, P=0.007, respectively).
Conclusion
GNAS mutations in GH-secreting pituitary tumors are associated with higher preoperative insulin-like growth factor-1 levels and surgical remission rates and lower immediate postoperative nadir GH levels. Thus, GNAS mutation status can predict surgical responsiveness in patients with acromegaly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Genetic diagnosis in acromegaly and gigantism: From research to clinical practice
Claudia Ramírez-Rentería, Laura C. Hernández-Ramírez
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; : 101892. CrossRef - CD8/PD-L1 immunohistochemical reactivity and gene alterations in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Haruto Nishida, Yoshihiko Kondo, Takahiro Kusaba, Kazuhiro Kawamura, Yuzo Oyama, Tsutomu Daa, Avaniyapuram Kannan Murugan
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(2): e0281647. CrossRef - Dynamic monitoring of circulating tumor DNA to analyze genetic characteristics and resistance profile of lorlatinib in ALK positive previously treated NSCLC
Xiya Ma, Kun Zhang, Jing Xu, Hongjun Gao, Shaoxing Yang, Haifeng Qin, Hong Wang, Fang Gao, Xiaoqing Liu
Thoracic Cancer.2023; 14(20): 1980. CrossRef - Multiomics Approach to Acromegaly: Unveiling Translational Insights for Precision Medicine
Kyungwon Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 463. CrossRef - Hotspots of Somatic Genetic Variation in Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors
Mariana Torres-Morán, Alexa L. Franco-Álvarez, Rosa G. Rebollar-Vega, Laura C. Hernández-Ramírez
Cancers.2023; 15(23): 5685. CrossRef
- Adrenal gland
- Diagnosis for Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Joint Position Statement of the Korean Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Task Force
-
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyung Ae Lee, Seung Hun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Yun Mi Choi, Namki Hong, A Ram Hong, Sang-Wook Kang, Byung Kwan Park, Moon-Woo Seong, Myungshin Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Chan Kwon Jung, Young Seok Cho, Jin Chul Paeng, Jae Hyeon Kim, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Yumie Rhee, Chong Hwa Kim, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):322-338. Published online April 6, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.908
-
-
7,512
View
-
572
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
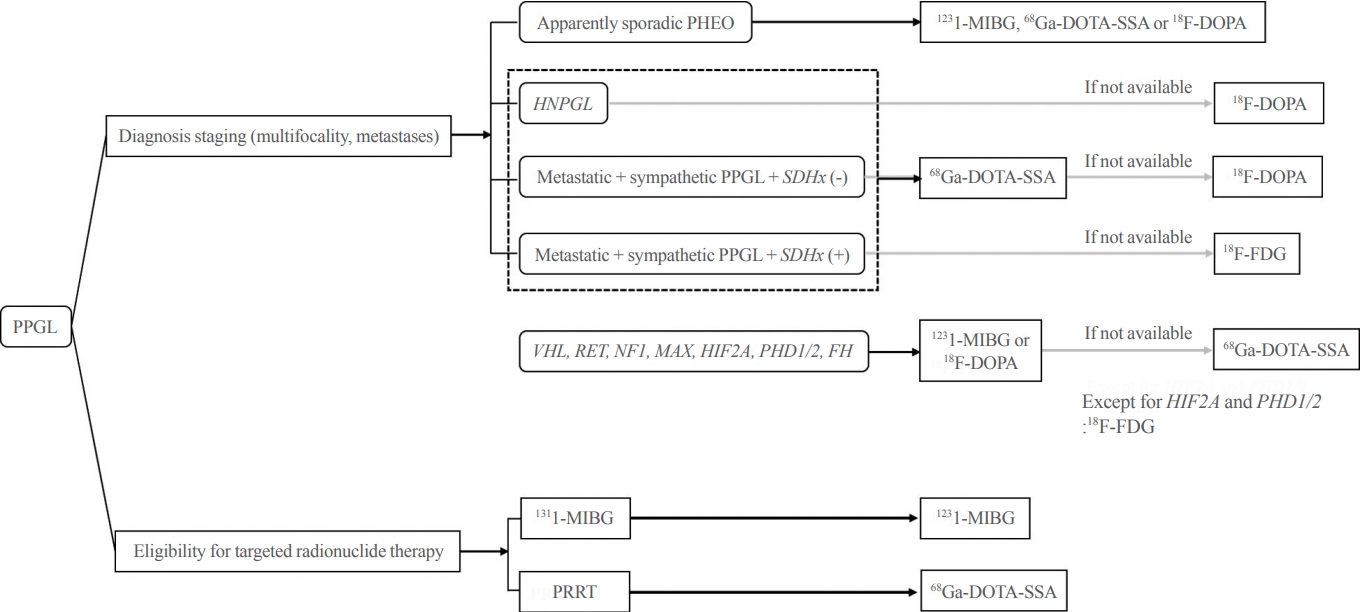
- Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGLs) are rare catecholamine-secreting neuroendocrine tumors but can be life-threatening. Although most PPGLs are benign, approximately 10% have metastatic potential. Approximately 40% cases are reported as harboring germline mutations. Therefore, timely and accurate diagnosis of PPGLs is crucial. For more than 130 years, clinical, molecular, biochemical, radiological, and pathological investigations have been rapidly advanced in the field of PPGLs. However, performing diagnostic studies to localize lesions and detect metastatic potential can be still challenging and complicated. Furthermore, great progress on genetics has shifted the paradigm of genetic testing of PPGLs. The Korean PPGL task force team consisting of the Korean Endocrine Society, the Korean Surgical Society, the Korean Society of Nuclear Medicine, the Korean Society of Pathologists, and the Korean Society of Laboratory Medicine has developed this position statement focusing on the comprehensive and updated diagnosis for PPGLs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Prospective Comparative Study of 18F-FDOPA PET/CT Versus 123I-MIBG Scintigraphy With SPECT/CT for the Diagnosis of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma
Changhwan Sung, Hyo Sang Lee, Dong Yun Lee, Yong-il Kim, Jae Eun Kim, Sang Ju Lee, Seung Jun Oh, Tae-Yon Sung, Yu-Mi Lee, Young Hoon Kim, Beom-Jun Kim, Jung-Min Koh, Seung Hun Lee, Jin-Sook Ryu
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2024; 49(1): 27. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: A Position Statement of the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Ho-Cheol Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 175. CrossRef - Lesion-based indicators predict long-term outcomes of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma– SIZEPASS
Helena Hanschell, Salvador Diaz-Cano, Alfredo Blanes, Nadia Talat, Gabriele Galatá, Simon Aylwin, Klaus Martin Schulte
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Interleukin-6-producing paraganglioma as a rare cause of systemic inflammatory response syndrome: a case report
Yin Young Lee, Seung Min Chung
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2023; 40(4): 435. CrossRef - (Extremely rare intrapericardial location of paraganglioma)
Jaroslav Zajíc, Aleš Mokráček, Ladislav Pešl, Jiří Haniš, Dita Schaffelhoferová
Cor et Vasa.2023; 65(4): 692. CrossRef - A Case of Von Hippel-Lindau Disease With Recurrence of Paraganglioma and No Other Associated Symptoms: The Importance of Genetic Testing and Establishing Follow-Up Policies
Naoki Okada, Akihiro Shioya, Sumihito Togi, Hiroki Ura, Yo Niida
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - KSNM60 in Nuclear Endocrinology: from the Beginning to the Future
Chae Moon Hong, Young Jin Jeong, Hae Won Kim, Byeong-Cheol Ahn
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2022; 56(1): 17. CrossRef - Change of Computed Tomography-Based Body Composition after Adrenalectomy in Patients with Pheochromocytoma
Yousun Ko, Heeryoel Jeong, Seungwoo Khang, Jeongjin Lee, Kyung Won Kim, Beom-Jun Kim
Cancers.2022; 14(8): 1967. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: a Position Statement from the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Hwa Young Ahn, Bu Kyung Kim, Seong Hee Ahn, So Young Park, Min-Hee Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Sun Wook Cho, Ho-Cheol Kang
International Journal of Thyroidology.2022; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - Pheochromocytoma with Retroperitoneal Metastasis: A Case Report
建新 崔
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2021; 11(05): 2239. CrossRef
- Endocrine Research
- Danshen Extracts Prevents Obesity and Activates Mitochondrial Function in Brown Adipose Tissue
-
Yoon Hee Cho, Cheol Ryong Ku, Young-Suk Choi, Hyeon Jeong Lee, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):185-195. Published online February 24, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.835
-
-
4,619
View
-
132
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
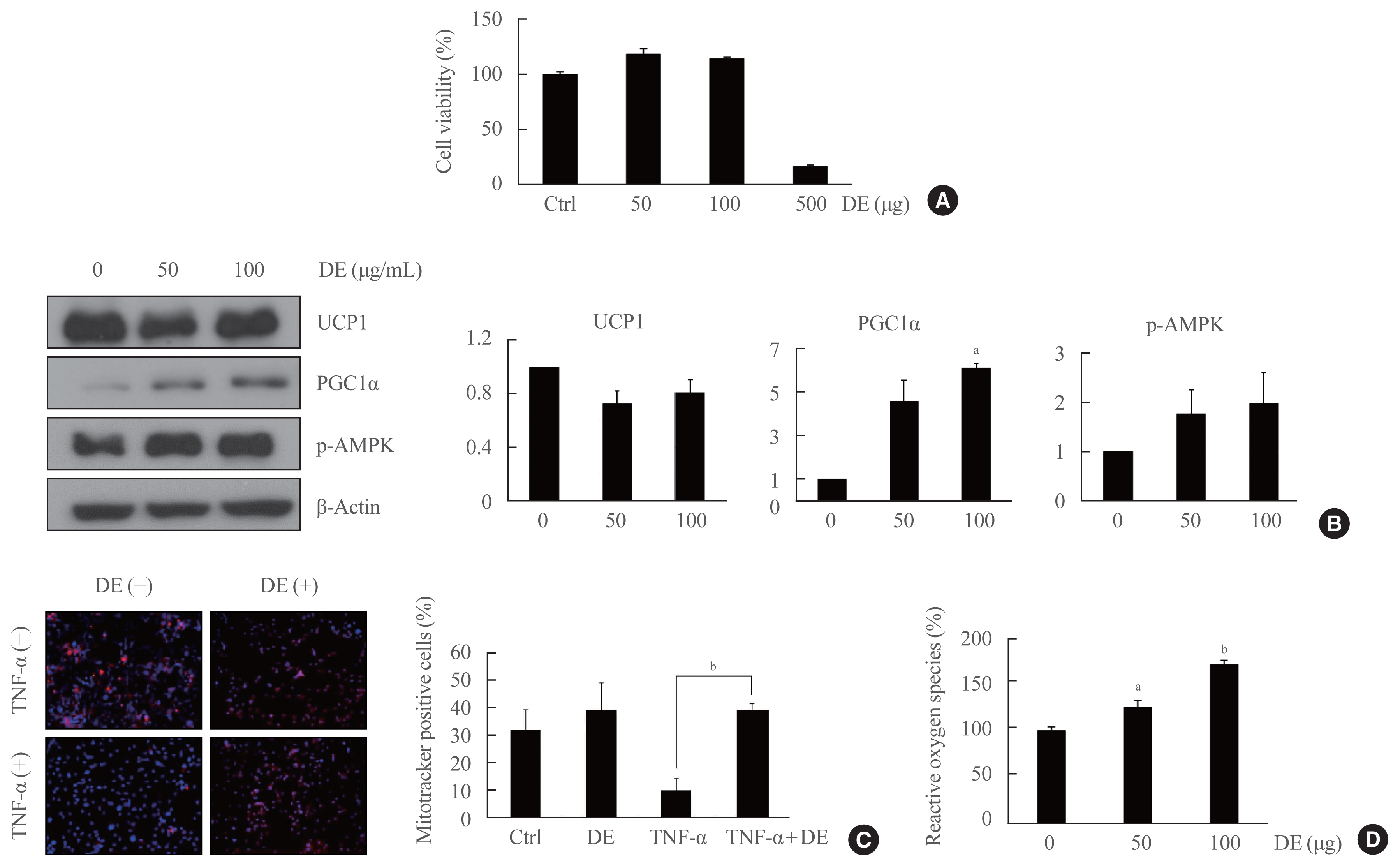
Danshen has been widely used in oriental medicine to improve body function. The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of water-soluble Danshen extract (DE) on weight loss and on activation proteins involved in mitochondrial biogenesis in brown adipose tissue (BAT) in obese mice.
Methods
BAT was isolated from 7-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats, and expression of proteins related to mitochondrial biogenesis was confirmed in both brown preadipocytes and mature brown adipocytes treated with DE. For the in vivo study, low-density lipoprotein receptor knock out mice were divided into three groups and treated for 17 weeks with: standard diet; high fat diet (HFD); HFD+DE. Body weight was measured every week, and oral glucose tolerance test was performed after DE treatment in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. To observe the changes in markers related to thermogenesis and adipogenesis in the BAT, white adipose tissue (WAT) and liver of experimental animals, tissues were removed and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen.
Results
DE increased the expression of uncoupling protein 1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha in brown preadipocytes, and also promoted the brown adipocyte differentiation and mitochondrial function in the mature brown adipocytes. Reactive oxygen species production in brown preadipocytes was increased depending on the concentration of DE. DE activates thermogenesis in BAT and normalizes increased body weight and adipogenesis in the liver due to HFD. Browning of WAT was increased in WAT of DE treatment group.
Conclusion
DE protects against obesity and activates mitochondrial function in BAT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Pharmacological Benefits and Underlying Mechanisms of Salvia miltiorrhiza against Molecular Pathology of Various Liver Diseases: A Review
Cho Hyun Hwang, Eungyeong Jang, Jang-Hoon Lee
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.2023; 51(07): 1675. CrossRef
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
- Precision Therapy in Acromegaly Caused by Pituitary Tumors: How Close Is It to Reality?
-
Cheol Ryong Ku, Vladimir Melnikov, Zhaoyun Zhang, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):206-216. Published online June 24, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.206
-
-
6,734
View
-
250
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
8
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
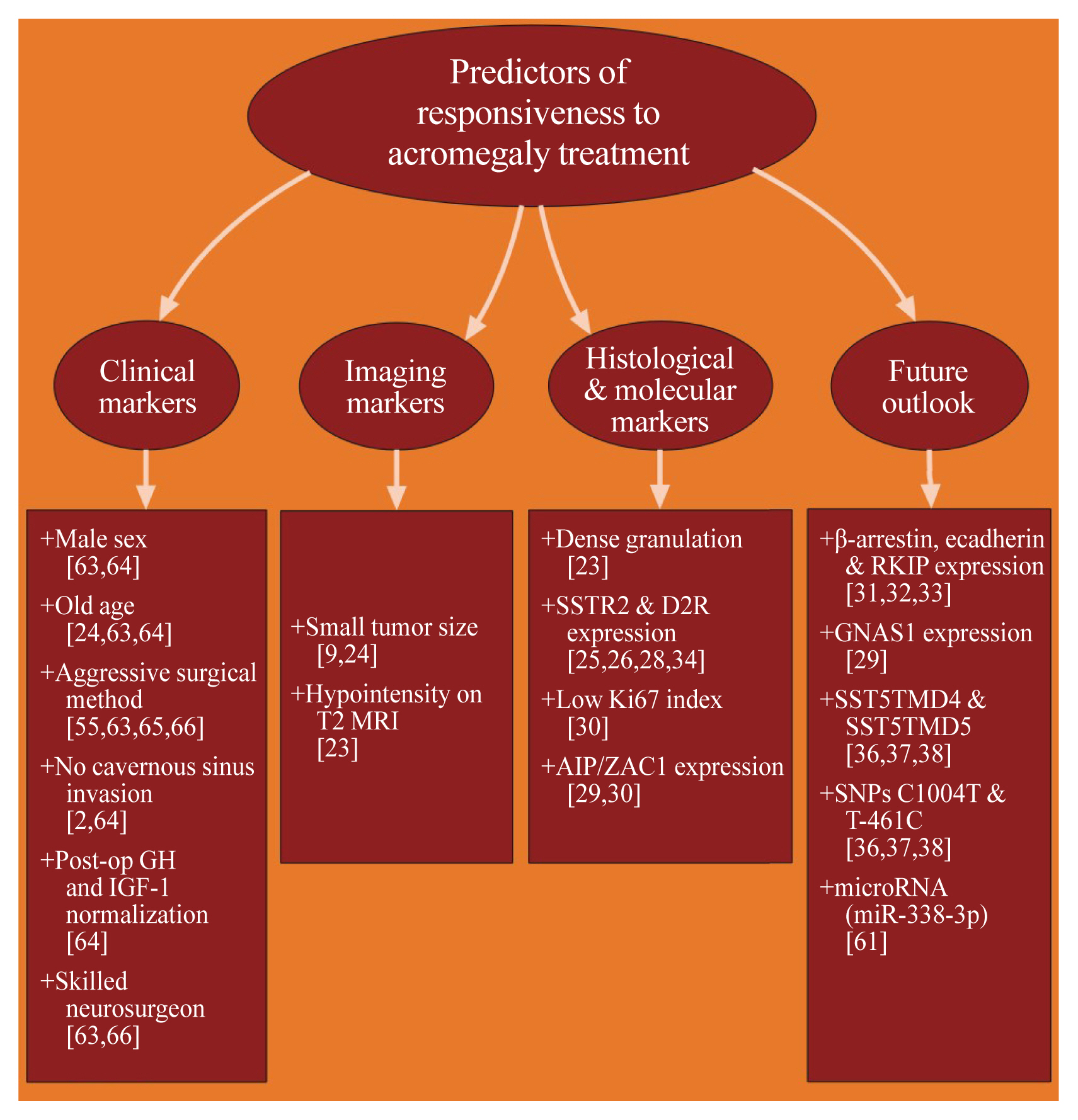
- Acromegaly presents with an enigmatic range of symptoms and comorbidities caused by chronic and progressive growth hormone elevations, commonly due to endocrinologic hypersecretion from a pituitary gland tumor. Comprehensive national acromegaly databases have been appearing over the years, allowing for international comparisons of data, although still presenting varying prevalence and incidence rates. Lack of large-scale analysis in geographical and ethnic differences in clinical presentation and management requires further research. Assessment of current and novel predictors of responsiveness to distinct therapy can lead to multilevel categorization of patients, allowing integration into new clinical guidelines and reduction of increased morbidity and mortality associated with acromegaly. This review compares current data from epidemiological studies and assesses the present-day application of prognostic factors in medical practice, the reality of precision therapy, as well as its future prospects in acromegaly, with a special focus on its relevance to the South Korean population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Biomarkers of response to treatment in acromegaly
Leandro Kasuki, Elisa Lamback, Ximene Antunes, Mônica R. Gadelha
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 19(1): 71. CrossRef - Multiomics Approach to Acromegaly: Unveiling Translational Insights for Precision Medicine
Kyungwon Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 463. CrossRef - Risk of depression in patients with acromegaly in Korea (2006-2016): a nationwide population-based study
Shinje Moon, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
European Journal of Endocrinology.2023; 189(3): 363. CrossRef - The Future of Somatostatin Receptor Ligands in Acromegaly
Monica R Gadelha, Luiz Eduardo Wildemberg, Leandro Kasuki
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(2): 297. CrossRef - Innovative therapeutics in acromegaly
Leandro Kasuki, Mônica R. Gadelha
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 36(6): 101679. CrossRef - Risk of Neurodegenerative Diseases in Patients With Acromegaly
Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Kyung-Soo Kim, Cheol-Young Park
Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning-based Prediction Model for Treatment of Acromegaly With First-generation Somatostatin Receptor Ligands
Luiz Eduardo Wildemberg, Aline Helen da Silva Camacho, Renan Lyra Miranda, Paula C L Elias, Nina R de Castro Musolino, Debora Nazato, Raquel Jallad, Martha K P Huayllas, Jose Italo S Mota, Tobias Almeida, Evandro Portes, Antonio Ribeiro-Oliveira, Lucio Vi
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(7): 2047. CrossRef - Skin anomalies in acromegalic patients (Review of the practical aspects)
Florica Sandru, Adelina Popa, Dan Paduraru, Alexandru Filipescu, Mara Carsote, Adina Ghemigian
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Miscellaneous
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Position Statement from Korean Endocrine Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology
-
Jung Hee Kim, Hyun Wook Chae, Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyeong Hye Park, Dong Jun Lim, Kwang Joon Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Gyuri Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Seong Hee Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Yul Hwangbo, Ju Hee Lee, Bu Kyung Kim, Yong Jun Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Hwa Young Ahn, Hoon Sung Choi, Sang Mo Hong, Dong Yeob Shin, Ji A Seo, Se Hwa Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Hoon Yu, Byung Joon Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sung-Woon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):272-287. Published online June 24, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.272
-
-
9,486
View
-
428
Download
-
13
Web of Science
-
15
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
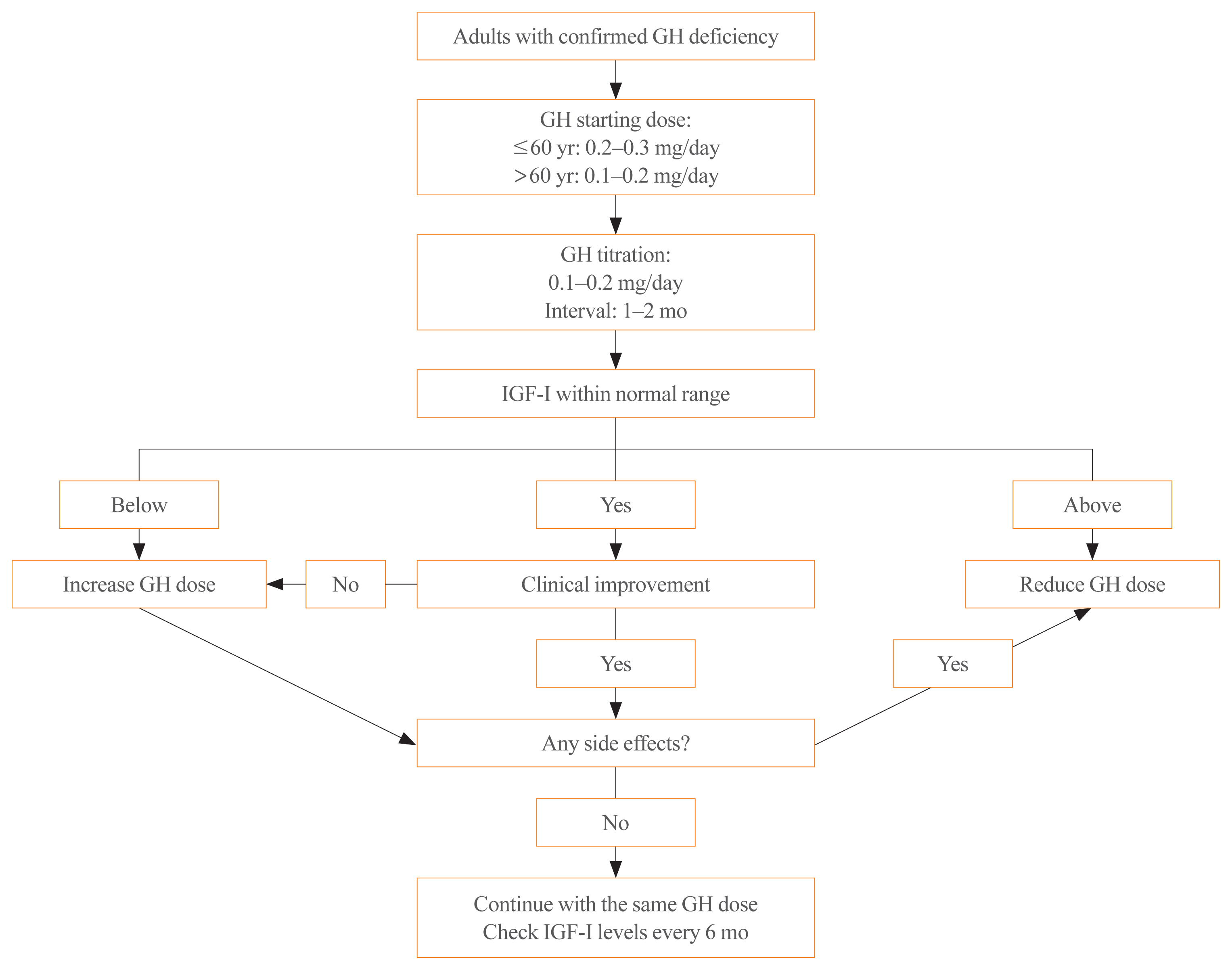
- Growth hormone (GH) deficiency is caused by congenital or acquired causes and occurs in childhood or adulthood. GH replacement therapy brings benefits to body composition, exercise capacity, skeletal health, cardiovascular outcomes, and quality of life. Before initiating GH replacement, GH deficiency should be confirmed through proper stimulation tests, and in cases with proven genetic causes or structural lesions, repeated GH stimulation testing is not necessary. The dosing regimen of GH replacement therapy should be individualized, with the goal of minimizing side effects and maximizing clinical improvements. The Korean Endocrine Society and the Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology have developed a position statement on the diagnosis and treatment of GH deficiency. This position statement is based on a systematic review of evidence and expert opinions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial
Ghina Tsurayya, Cut Alifiya Nazhifah, Muhammad Rahmat Pirwanja, Putri Oktaviani Zulfa, Muhammad Raihan Ramadhan Tatroman, Fajar Fakri, Muhammad Iqhrammullah
Children.2024; 11(2): 227. CrossRef - Evaluation of Adult Height in Patients with Non-Permanent Idiopathic GH Deficiency
Agnese Murianni, Anna Lussu, Chiara Guzzetti, Anastasia Ibba, Letizia Casula, Mariacarolina Salerno, Marco Cappa, Sandro Loche
Endocrines.2023; 4(1): 169. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests
Soo Yeun Sim, Moon Bae Ahn
Sensors.2023; 23(15): 6892. CrossRef - The risk patients with AGHD have of developing CVD
Eisha Javed, Maha Zehra, Naz Elahi
International Journal of Cardiology Cardiovascular Risk and Prevention.2023; 19: 200221. CrossRef - Diagnosis of GH Deficiency Without GH Stimulation Tests
Anastasia Ibba, Sandro Loche
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Impacts of Discontinuation and Resumption of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Treatment during the Transition Period in Patients with Childhood-Onset Growth Hormone Deficiency
Yun Jeong Lee, Yunha Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Han Saem Choi, Ho-Seong Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Jung Eun Moon, Cheol Woo Ko, Moon Bae Ahn, Byung-Kyu Suh, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 359. CrossRef - A Radiomics-Based Model with the Potential to Differentiate Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature on Sella MRI
Taeyoun Lee, Kyungchul Song, Beomseok Sohn, Jihwan Eom, Sung Soo Ahn, Ho-Seong Kim, Seung-Koo Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(9): 856. CrossRef - Phenotypic spectrum of patients with mutations in CHD7: clinical implications of endocrinological findings
Ja Hye Kim, Yunha Choi, Soojin Hwang, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Endocrine Disorders: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Hyemi Kwon, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Hee Kyung Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 839. CrossRef - Laron syndrome: clinic, diagnostics (а clinical case)
P.M. Lіashuk, R.P. Lіashuk, N.I. Stankova, M.B. Kudina
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(3): 193. CrossRef - Diagnosis for Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Joint Position Statement of the Korean Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Task Force
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyung Ae Lee, Seung Hun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Yun Mi Choi, Namki Hong, A Ram Hong, Sang-Wook Kang, Byung Kwan Park, Moon-Woo Seong, Myungshin Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 322. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation Guidelines for Adrenal Tumor Ablation
Byung Kwan Park, Masashi Fujimori, Shu-Huei Shen, Uei Pua
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 553. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation guidelines for renal cell carcinoma
Byung Kwan Park, Shu-Huei Shen, Masashi Fujimori, Yi Wang
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2021; 62(4): 378. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency
Jung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2021; 96(5): 400. CrossRef
- Endocrine Research
- Therapeutic Effect of a Novel Chimeric Molecule Targeting Both Somatostatin and Dopamine Receptors on Growth Hormone-Secreting Pituitary Adenomas
-
Jean Kim, Ju Hun Oh, Heather Harlem, Michael D. Culler, Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):177-187. Published online March 19, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.177
-
-
4,501
View
-
106
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Acromegaly is a rare disease primarily caused by growth hormone (GH)-secreting pituitary adenomas, and its treatment is costly. Moreover, some patients are unresponsive to treatment. Hence, there are increasing efforts to develop new drugs with improved effectiveness for this disease. BIM23B065 is a novel chimeric molecule that acts on both somatostatin and dopamine receptors. This study aimed to investigate the effects of BIM23B065 compared with those of a somatostatin receptor analog and a dopamine agonist. MethodsThe effects of BIM23B065 on the proliferation, GH and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) levels, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and cyclic AMP response element binding (CREB) phosphorylation of GH3 cells were investigated with MTS assay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and Western blotting, respectively. The dosage and treatment duration of BIM23B065 were tested in animal models of GH-secreting pituitary adenoma. The effect of BIM23B065 (3 mg/kg/day) on changes in IGF-1 levels before and after treatment was further investigated. ResultsIn vitro, BIM23B065 treatment decreased GH release in the culture media and downregulated ERK 1/2 and CREB phosphorylation to 22% and 26%, respectively. In vivo, IGF-1 expression decreased to 50 % after 4 weeks of treatment with BIM23B065 using an osmotic pump implant. Moreover, magnetic resonance imaging results showed that the tumor size decreased significantly following treatment with BIM23B065 for 4 weeks. ConclusionThe novel chimeric molecule was effective in decreasing IGF-1 and GH levels and may serve as an effective therapeutic agent for acromegaly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Pituitary Tumorigenesis—Implications for Management
Rodanthi Vamvoukaki, Maria Chrysoulaki, Grigoria Betsi, Paraskevi Xekouki
Medicina.2023; 59(4): 812. CrossRef - Current and Emerging Medical Therapies in Pituitary Tumors
Nicolas Sahakian, Frédéric Castinetti, Thierry Brue, Thomas Cuny
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(4): 955. CrossRef - Characterization of the ability of a, second-generation SST-DA chimeric molecule, TBR-065, to suppress GH secretion from human GH-secreting adenoma cells
Thomas Cuny, Thomas Graillon, Célines Defilles, Rakesh Datta, Shengwen Zhang, Dominique Figarella-Branger, Henry Dufour, Grégory Mougel, Thierry Brue, Tanya Landsman, Heather A. Halem, Michael D. Culler, Anne Barlier, Alexandru Saveanu
Pituitary.2021; 24(3): 351. CrossRef - Efficacy of a Novel Second-Generation Somatostatin-Dopamine Chimera (TBR-065) in Human Medullary Thyroid Cancer: A Preclinical Study
Alessandra Dicitore, Maria Celeste Cantone, Germano Gaudenzi, Davide Saronni, Silvia Carra, Maria Orietta Borghi, Manuela Albertelli, Diego Ferone, Leo J. Hofland, Luca Persani, Giovanni Vitale
Neuroendocrinology.2021; 111(10): 937. CrossRef - Emerging drugs for the treatment of acromegaly
Claudia Campana, Giuliana Corica, Federica Nista, Francesco Cocchiara, Giulia Graziani, Keyvan Khorrami, Marta Franco, Mara Boschetti, Diego Ferone, Federico Gatto
Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs.2020; 25(4): 409. CrossRef
- Endocrine Research
- Effects of Oxytocin on Cell Proliferation in a Corticotroph Adenoma Cell Line
-
Jung Soo Lim, Young Woo Eom, Eun Soo Lee, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Ja-Young Kwon, Junjeong Choi, Choon Hee Chung, Young Suk Jo, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(3):302-313. Published online September 26, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.302
-
-
5,008
View
-
74
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Oxytocin (OXT) has been reported to act as a growth regulator in various tumor cells. However, there is a paucity of data on the influence of OXT on cell proliferation of corticotroph adenomas. This study aimed to examine whether OXT affects cell growth in pituitary tumor cell lines (AtT20 and GH3 cells) with a focus on corticotroph adenoma cells. MethodsReverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were conducted with AtT20 cells to confirm the effects of OXT on hormonal activity; flow cytometry was used to assess changes in the cell cycle after OXT treatment. Moreover, the impact of OXT on proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), nuclear factor κB, and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway was analyzed by Western blot. ResultsOXT treatment of 50 nM changed the gene expression of OXT receptor and pro-opiomelanocortin within a short time. In addition, OXT significantly reduced adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion within 1 hour. S and G2/M populations of AtT20 cells treated with OXT for 24 hours were significantly decreased compared to the control. Furthermore, OXT treatment decreased the protein levels of PCNA and phosphorylated extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (P-ERK) in AtT20 cells. ConclusionAlthough the cytotoxic effect of OXT in AtT20 cells was not definite, OXT may blunt cell proliferation of corticotroph adenomas by altering the cell cycle or reducing PCNA and P-ERK levels. Further research is required to investigate the role of OXT as a potential therapeutic target in corticotroph adenomas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Increased proliferation and neuronal fate in prairie vole brain progenitor cells cultured in vitro: effects by social exposure and sexual dimorphism
Daniela Ávila-González, Italo Romero-Morales, Lizette Caro, Alejandro Martínez-Juárez, Larry J. Young, Francisco Camacho-Barrios, Omar Martínez-Alarcón, Analía E. Castro, Raúl G. Paredes, Néstor F. Díaz, Wendy Portillo
Biology of Sex Differences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anterior pituitary gland synthesises dopamine from l‐3,4‐dihydroxyphenylalanine (l‐dopa)
Santiago Jordi Orrillo, Nataly de Dios, Antonela Sofía Asad, Fernanda De Fino, Mercedes Imsen, Ana Clara Romero, Sandra Zárate, Jimena Ferraris, Daniel Pisera
Journal of Neuroendocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
- Medical Treatment with Somatostatin Analogues in Acromegaly: Position Statement
-
Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Byung Joon Kim, Sung-Woon Kim, Kyeong Hye Park, Kee Ho Song, Seungjoon Oh, Hyun Koo Yoon, Eun Jig Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Dong Jun Lim, Dong Yeob Shin, Se Hwa Kim, Min Jeong Kwon, Ha Young Kim, Jin Hwa Kim, Dong Sun Kim, Chong Hwa Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):53-62. Published online March 21, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.53
-
-
6,459
View
-
253
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
11
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
The Korean Endocrine Society (KES) published clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acromegaly in 2011. Since then, the number of acromegaly cases, publications on studies addressing medical treatment of acromegaly, and demands for improvements in insurance coverage have been dramatically increasing. In 2017, the KES Committee of Health Insurance decided to publish a position statement regarding the use of somatostatin analogues in acromegaly. Accordingly, consensus opinions for the position statement were collected after intensive review of the relevant literature and discussions among experts affiliated with the KES, and the Korean Neuroendocrine Study Group. This position statement includes the characteristics, indications, dose, interval (including extended dose interval in case of lanreotide autogel), switching and preoperative use of somatostatin analogues in medical treatment of acromegaly. The recommended approach is based on the expert opinions in case of insufficient clinical evidence, and where discrepancies among the expert opinions were found, the experts voted to determine the recommended approach. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Hydrogel-fiber-mesh-based 3D cell cultures: A new method for studying pituitary tumors
Wooju Jeong, Sungrok Wang, Yumin Kim, Soohyun Lee, Minhu Huang, Jaeil Park, Myung-Han Yoon, Chang-Myung Oh, Cheol Ryong Ku
Smart Materials in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: A Position Statement of the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Ho-Cheol Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 175. CrossRef - Growth Hormone Excess: Implications and Management
Suneela Dhaneshwar, Shrishti Shandily, Vatsalya Tiwari
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2023; 23(6): 748. CrossRef - Revisiting the usefulness of the short acute octreotide test to predict treatment outcomes in acromegaly
Montserrat Marques-Pamies, Joan Gil, Elena Valassi, Marta Hernández, Betina Biagetti, Olga Giménez-Palop, Silvia Martínez, Cristina Carrato, Laura Pons, Rocío Villar-Taibo, Marta Araujo-Castro, Concepción Blanco, Inmaculada Simón, Andreu Simó-Servat, Gemm
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: a Position Statement from the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Hwa Young Ahn, Bu Kyung Kim, Seong Hee Ahn, So Young Park, Min-Hee Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Sun Wook Cho, Ho-Cheol Kang
International Journal of Thyroidology.2022; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - Octreotide in the treatment of acromegaly – the possibilities of high-dose therapy
I. A. Ilovayskaya
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (10): 148. CrossRef - Approach of Acromegaly during Pregnancy
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mara Carsote, Ana Valea, Andreea Gabriela Nicola, Ionela Teodora Dascălu, Tiberiu Tircă, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Mihaela Jana Țuculină
Diagnostics.2022; 12(11): 2669. CrossRef - Left to themselves: Time to target chronic pain in childhood rare diseases
Christine B. Sieberg, Alyssa Lebel, Erin Silliman, Scott Holmes, David Borsook, Igor Elman
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2021; 126: 276. CrossRef - Severe respiratory failure in a patient with COVID-19 and acromegaly: rapid improvement after adding octreotide
Jacob Luty, LesleAnn Hayward, Melanie Jackson, P Barton Duell
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(8): e243900. CrossRef - Precision Therapy in Acromegaly Caused by Pituitary Tumors: How Close Is It to Reality?
Cheol Ryong Ku, Vladimir Melnikov, Zhaoyun Zhang, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 206. CrossRef - Medical Treatment with Somatostatin Analogues in Acromegaly: Position Statement
Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Byung Joon Kim, Sung-Woon Kim, Kyeong Hye Park, Kee Ho Song, Seungjoon Oh, Hyun Koo Yoon, Eun Jig Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Dong
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2019; 94(6): 485. CrossRef
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Response: The Effects of High Fat Diet and Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Activity of Brown Adipocytes (Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:328-35, Cheol Ryong Ku et al.)
-
Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):482-483. Published online September 26, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.482
-
-
2,592
View
-
26
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Mitochondrial oxidative stress in obesity: role of the mineralocorticoid receptor
Clara Lefranc, Malou Friederich-Persson, Roberto Palacios-Ramirez, Aurelie Nguyen Dinh Cat
Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 238(3): R143. CrossRef
- Endocrine Research
- The Effects of High Fat Diet and Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Activity of Brown Adipocytes
-
Cheol Ryong Ku, Yoon Hee Cho, Zhen-Yu Hong, Ha Lee, Sue Ji Lee, Seung-soo Hong, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(2):328-335. Published online April 8, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.328
-
-
4,148
View
-
50
Download
-
25
Web of Science
-
25
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Resveratrol (RSV) is a polyphenolic phytoalexin that has many effects on metabolic diseases such as diabetes and obesity. Given the importance of brown adipose tissue (BAT) for energy expenditure, we investigated the effects of RSV on brown adipocytes. MethodsFor the in vitro study, interscapular BAT was isolated from 7-week-old male Sprague Dawley rats. For the in vivo study, 7-week-old male Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats were divided into four groups and treated for 27 weeks with: standard diet (SD); SD+RSV (10 mg/kg body weight, daily); high fat diet (HFD); HFD+RSV. RSV was provided via oral gavage once daily during the in vivo experiments. ResultsRSV treatment of primary cultured brown preadipocytes promoted mitochondrial activity, along with over-expression of estrogen receptor α (ER-α). In OLETF rats, both HFD and RSV treatment increased the weight of BAT and the differentiation of BAT. However, only RSV increased the mitochondrial activity and ER-α expression of BAT in the HFD-fed group. Finally, RSV improved the insulin sensitivity of OLETF rats by increasing the mitochondrial activity of BAT, despite having no effects on white adipocytes and muscles in either diet group. ConclusionRSV could improve insulin resistance, which might be associated with mitochondrial activity of brown adipocyte. Further studies evaluating the activity of RSV for both the differentiation and mitochondrial activity of BAT could be helpful in investigating the effects of RSV on metabolic parameters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Natural Bioactive Compounds from Foods Inhibited Pigmentation Especially Potential Application of Fucoxanthin to Chloasma: a Mini-Review
Yida Wang, Hang Qi
Food Reviews International.2024; 40(1): 20. CrossRef - Resveratrol combats chronic diseases through enhancing mitochondrial quality
Weichu Tao, Hu Zhang, Xia Jiang, Ning Chen
Food Science and Human Wellness.2024; 13(2): 597. CrossRef - The Potential to Fight Obesity with Adipogenesis Modulating Compounds
Jiaqi Zhao, Ailin Zhou, Wei Qi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(4): 2299. CrossRef - Macrophage and Adipocyte Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Obesity-Induced Metabolic Diseases
Liwen Wang, Jie Hu, Haiyan Zhou
The World Journal of Men's Health.2021; 39(4): 606. CrossRef - Precision Nutrition to Activate Thermogenesis as a Complementary Approach to Target Obesity and Associated-Metabolic-Disorders
Marina Reguero, Marta Gómez de Cedrón, Sonia Wagner, Guillermo Reglero, José Carlos Quintela, Ana Ramírez de Molina
Cancers.2021; 13(4): 866. CrossRef - Natural Antioxidant Application on Fat Accumulation: Preclinical Evidence
Proshanta Roy, Daniele Tomassoni, Enea Traini, Ilenia Martinelli, Maria Vittoria Micioni Di Bonaventura, Carlo Cifani, Francesco Amenta, Seyed Khosrow Tayebati
Antioxidants.2021; 10(6): 858. CrossRef - Activation of Brown Adipose Tissue and Promotion of White Adipose Tissue Browning by Plant-based Dietary Components in Rodents: A Systematic Review
Francisco J Osuna-Prieto, Borja Martinez-Tellez, Antonio Segura-Carretero, Jonatan R Ruiz
Advances in Nutrition.2021; 12(6): 2147. CrossRef - Role of Dietary Polyphenols in Adipose Tissue Browning: A Narrative Review
Juan Salazar, Clímaco Cano, José L. Pérez, Ana Castro, María P. Díaz, Bermary Garrido, Rubén Carrasquero, Maricarmen Chacín, Manuel Velasco, Luis D´Marco, Joselyn Rojas-Quintero, Valmore Bermúdez
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2020; 26(35): 4444. CrossRef - Brown and Brite: The Fat Soldiers in the Anti-obesity Fight
Shireesh Srivastava, Richard L. Veech
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of resveratrol on adipokines and myokines involved in fat browning: Perspectives in healthy weight against obesity
Oh Yoen Kim, Ji Yeon Chung, Juhyun Song
Pharmacological Research.2019; 148: 104411. CrossRef - Ginsenoside Rb2 Alleviates Obesity by Activation of Brown Fat and Induction of Browning of White Fat
Yilian Hong, Yi Lin, Qiya Si, Lijuan Yang, Weisong Dong, Xuejiang Gu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Programming of the Beige Phenotype in White Adipose Tissue of Adult Mice by Mild Resveratrol and Nicotinamide Riboside Supplementations in Early Postnatal Life
Alba Serrano, Madhu Asnani-Kishnani, Ana María Rodríguez, Andreu Palou, Joan Ribot, María Luisa Bonet
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Polyphenols on Thermogenesis and Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Tanila Wood dos Santos, Quélita Cristina Pereira, Lucimara Teixeira, Alessandra Gambero, Josep A. Villena, Marcelo Lima Ribeiro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(9): 2757. CrossRef - Programming mediated by fatty acids affects uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) in brown adipose tissue
Perla P. Argentato, Helena de Cássia César, Débora Estadella, Luciana P. Pisani
British Journal of Nutrition.2018; 120(6): 619. CrossRef - Effects of Genistein on Differentiation and Viability of Human Visceral Adipocytes
Elena Grossini, Serena Farruggio, Giulia Raina, David Mary, Giacomo Deiro, Sergio Gentilli
Nutrients.2018; 10(8): 978. CrossRef - A comprehensive review of the health perspectives of resveratrol
Abdur Rauf, Muhammad Imran, Hafiz Ansar Rasul Suleria, Bashir Ahmad, Dennis G. Peters, Mohammad S. Mubarak
Food & Function.2017; 8(12): 4284. CrossRef - The Role of Circulating Slit2, the One of the Newly Batokines, in Human Diabetes Mellitus
Yea Eun Kang, Sorim Choung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(3): 383. CrossRef - A nutritional perspective on UCP1-dependent thermogenesis
M. Luisa Bonet, Josep Mercader, Andreu Palou
Biochimie.2017; 134: 99. CrossRef - The Beneficial Effects of Quercetin, Curcumin, and Resveratrol in Obesity
Yueshui Zhao, Bo Chen, Jing Shen, Lin Wan, Yinxin Zhu, Tao Yi, Zhangang Xiao
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Antiobesity effects of resveratrol: which tissues are involved?
Alfredo Fernández‐Quintela, Iñaki Milton‐Laskibar, Marcela González, Maria P. Portillo
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.2017; 1403(1): 118. CrossRef - Resveratrol attenuates triglyceride accumulation associated with upregulation of Sirt1 and lipoprotein lipase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Haruki Imamura, Daiji Nagayama, Noriko Ishihara, Syo Tanaka, Rena Watanabe, Yasuhiro Watanabe, Yuta Sato, Takashi Yamaguchi, Noriko Ban, Hidetoshi Kawana, Masahiro Ohira, Kei Endo, Atsuhito Saiki, Kohji Shirai, Ichiro Tatsuno
Molecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports.2017; 12: 44. CrossRef - Resveratrol has dose-dependent effects on DNA fragmentation and mitochondrial activity of ovine secondary follicles cultured in vitro
T.J.S. Macedo, V.R.P. Barros, A.P.O. Monte, B.B. Gouveia, M.É.S. Bezerra, A.Y.P. Cavalcante, R.S. Barberino, V.G. Menezes, M.H.T. Matos
Zygote.2017; 25(4): 434. CrossRef - Response: The Effects of High Fat Diet and Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Activity of Brown Adipocytes (Endocrinol Metab2016;31:328-35, Cheol Ryong Ku et al.)
Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 482. CrossRef - Letter: The Effects of High Fat Diet and Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Activity of Brown Adipocytes (Endocrinol Metab2016;31:328-35, Cheol Ryong Ku et al.)
Ji-Young Cha
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 480. CrossRef
- Adrenal gland
- Clinical Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cushing's Disease in Korea
-
Kyu Yeon Hur, Jung Hee Kim, Byung Joon Kim, Min-Seon Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Sung-Woon Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):7-18. Published online March 27, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.7
-
-
6,703
View
-
151
Download
-
10
Web of Science
-
15
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
Cushing's disease (CD) is a rare disorder characterized by the overproduction of adrenocorticotropic hormone due to a pituitary adenoma that ultimately stimulates excessive cortisol secretion from the adrenal glands. Prior to the detection of pituitary adenomas, various clinical signs of CD such as central obesity, moon face, hirsutism, and facial plethora are usually already present. Uncontrolled hypercortisolism is associated with metabolic, cardiovascular, and psychological disorders that result in increased mortality. Hence, the early detection and treatment of CD are not only important but mandatory. Because its clinical manifestations vary from patient to patient and are common in other obesity-related conditions, the precise diagnosis of CD can be problematic. Thus, the present set of guidelines was compiled by Korean experts in this field to assist clinicians with the screening, diagnoses, and treatment of patients with CD using currently available tests and treatment modalities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Diet quality and dietary acid load in relation to cardiovascular disease mortality: Results from Fasa PERSIAN cohort study
Sahar Fereidouni, Najmeh Hejazi, Reza Homayounfar, Mojtaba Farjam
Food Science & Nutrition.2023; 11(3): 1563. CrossRef - Role of computed tomography in predicting adrenal adenomas with cortisol hypersecretion
Chan Kyo Kim, Kyung A Kang, Young Lyun Oh, Sung Yoon Park
The British Journal of Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary acid load and mortality from all causes, CVD and cancer: results from the Golestan Cohort Study
Ehsan Hejazi, Hadi Emamat, Maryam Sharafkhah, Atoosa Saidpour, Hossein Poustchi, Sadaf Sepanlou, Masoud Sotoudeh, Sanford Dawsey, Paolo Boffetta, Christian C Abnet, Farin Kamangar, Arash Etemadi, Akram Pourshams, Akbar Fazeltabar Malekshah, Paul Berennan,
British Journal of Nutrition.2022; 128(2): 237. CrossRef - Forty Years Together, New Leap Forward! The 40th Anniversary of the Korean Endocrine Society
Jong Chul Won, Ki-Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 851. CrossRef - Pituitary adenomas: current principles of diagnosis and treatment
L. I. Astafyeva, I. V. Chernov, I. V. Chekhonin, E. I. Shults, I. N. Pronin, P. L. Kalinin
Russian journal of neurosurgery.2021; 22(4): 94. CrossRef - Metabolic changes in serum steroids for diagnosing and subtyping Cushing’s syndrome
Chang Ho Ahn, Chaelin Lee, Jaeyoon Shim, Sung Hye Kong, Su-jin Kim, Yong Hwy Kim, Kyu Eun Lee, Chan Soo Shin, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2021; 210: 105856. CrossRef - Application of different variants of endoscopic transphenoidal removal of corticotropinomas in order to increase the frequency and duration of remission
A. Ashraf, I. V. Chernov, A. N. Shkarubo, M. A. Kutin, D. V. Fomichev, O. I. Sharipov, Yu. Yu. Trunin, D. N. Andreev, A. A. Abdilatipov, L. I. Astafieva, B. Abdali, A. B. Kurnosov, G. E. Chmutin, Kalinin P. L. Kalinin P. L.
Vestnik nevrologii, psihiatrii i nejrohirurgii (Bulletin of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery).2021; (2): 143. CrossRef - Modern aspects of surgery for cushing’s disease
A. Abdali, L.I. Astafeva, Yu.Yu. Trunin, I.V. Chernov, Yu.G. Sidneva, A.A. Abdilatipov, P.L. Kalinin
Voprosy neirokhirurgii imeni N.N. Burdenko.2021; 85(4): 111. CrossRef - Pituitary microadenomas — current diagnostic and treatment methods
L.I. Astafyeva, B.A. Kadashev, Yu.G. Sidneva, I.V. Chernov, P.L. Kalinin
Voprosy neirokhirurgii imeni N.N. Burdenko.2020; 84(2): 110. CrossRef - Usefulness of prolactin measurement in inferior petrosal sinus sampling with desmopressin for Cushing’s syndrome
Hamideh Akbari, Mohammad Ghorbani, Maryam Kabootari, Ali Zare Mehrjardi, Mohammad Reza Mohajeri Tehrani, Mojtaba Malek, Mohammad E. Khamseh
British Journal of Neurosurgery.2020; 34(3): 253. CrossRef - Hormonal aggressiveness according to the expression of cellular markers in corticotroph adenomas
Jung Soo Lim, Mi-Kyung Lee, Eunhee Choi, Namki Hong, Soo Il Jee, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrine.2019; 64(1): 147. CrossRef - Clinical Parameters to Distinguish Silent Corticotroph Adenomas from Other Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas
Daham Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Se Hee Park, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
World Neurosurgery.2018; 115: e464. CrossRef - Blood Tests for the Diagnosis of Adrenal Diseases
Seon-Ah Cha, Sung-Dae Moon
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2018; 93(6): 532. CrossRef - Choosing wisely: la lista del gruppo di studio Endocrinologia e Malattie del Metabolismo della Società Italiana di Patologia Clinica e Medicina di Laboratorio
Romolo M. Dorizzi, Anna Ferrari, Marina Vitillo, Beatrice Caruso, Claudio Cocco, Erennio Ciotoli, Federica D’Aurizio, Elisa Esposito, Germana Giannone, Giulio Ozzola, Ottavia Porzio, Emanuela Toffalori, Renato Tozzoli
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio - Italian Journal of Laboratory Medicine.2016; 12(2): 81. CrossRef - Surgical management of adrenocorticotropic hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas
Edwin S Kulubya, Daniel A Donoho, John D Carmichael, Gabriel Zada
International Journal of Endocrine Oncology.2016; 3(1): 41. CrossRef
- Adrenal gland
- Early Prediction of Long-Term Response to Cabergoline in Patients with Macroprolactinomas
-
Youngki Lee, Cheol Ryong Ku, Eui-Hyun Kim, Jae Won Hong, Eun Jig Lee, Sun Ho Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(3):280-292. Published online September 25, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.280
-
-
4,230
View
-
51
Download
-
12
Web of Science
-
13
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Cabergoline is typically effective for treating prolactinomas; however, some patients display cabergoline resistance, and the early characteristics of these patients remain unclear. We analyzed early indicators predicting long-term response to cabergoline. MethodsWe retrospectively reviewed the cases of 44 patients with macroprolactinomas who received cabergoline as first-line treatment; the patients were followed for a median of 16 months. The influence of various clinical parameters on outcomes was evaluated. ResultsForty patients (90.9%) were treated medically and displayed tumor volume reduction (TVR) of 74.7%, a prolactin normalization (NP) rate of 81.8%, and a complete response (CR; TVR >50% with NP, without surgery) rate of 70.5%. Most patients (93.1%) with TVR ≥25% and NP at 3 months eventually achieved CR, whereas only 50% of patients with TVR ≥25% without NP and no patients with TVR <25% achieved CR. TVR at 3 months was strongly correlated with final TVR (R=0.785). Patients with large macroadenomas exhibited a low NP rate at 3 months, but eventually achieved TVR and NP rates similar to those of patients with smaller tumors. Surgery independently reduced the final dose of cabergoline (β=-1.181 mg/week), and two of four patients who underwent surgery were able to discontinue cabergoline. ConclusionDetermining cabergoline response using TVR and NP 3 months after treatment is useful for predicting later outcomes. However, further cabergoline administration should be considered for patients with TVR >25% at 3 months without NP, particularly those with huge prolactinomas, because a delayed response may be achieved. As surgery can reduce the cabergoline dose necessary for successful disease control, it should be considered for cabergoline-resistant patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Resistance to dopamine agonists in the treatment of prolactinomas: diagnostic criteria, mechanisms and ways to overcome it
Irena A. Ilovayskaya, Gulnar R. Vagapova
Almanac of Clinical Medicine.2024; 51(7): 397. CrossRef - Diagnosis and management of prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas: a Pituitary Society international Consensus Statement
Stephan Petersenn, Maria Fleseriu, Felipe F. Casanueva, Andrea Giustina, Nienke Biermasz, Beverly M. K. Biller, Marcello Bronstein, Philippe Chanson, Hidenori Fukuoka, Monica Gadelha, Yona Greenman, Mark Gurnell, Ken K. Y. Ho, Jürgen Honegger, Adriana G.
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2023; 19(12): 722. CrossRef - Outcome Measures for Medical and Surgical Treatment of Prolactinomas. Is the Role of Surgery Underestimated?
Andrius Anuzis, Kevin O. Lillehei
Journal of Neurological Surgery Part B: Skull Base.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Are dopamine agonists still the first-choice treatment for prolactinoma in the era of endoscopy? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiangming Cai, Junhao Zhu, Jin Yang, Chao Tang, Zixiang Cong, Chiyuan Ma
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Italian Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AME) and International Chapter of Clinical Endocrinology (ICCE). Position statement for clinical practice: prolactin-secreting tumors
Renato Cozzi, Maria Rosaria Ambrosio, Roberto Attanasio, Claudia Battista, Alessandro Bozzao, Marco Caputo, Enrica Ciccarelli, Laura De Marinis, Ernesto De Menis, Marco Faustini Fustini, Franco Grimaldi, Andrea Lania, Giovanni Lasio, Francesco Logoluso, M
European Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 186(3): P1. CrossRef - Biochemical Remission after Cabergoline Withdrawal in Hyperprolactinemic Patients with Visible Remnant Pituitary Adenoma
Kyungwon Kim, Yae Won Park, Daham Kim, Sung Soo Ahn, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Cheol Ryong Ku
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(2): e615. CrossRef - Surgery is a safe, effective first-line treatment modality for noninvasive prolactinomas
Ji Yong Park, Wonsuk Choi, A Ram Hong, Jee Hee Yoon, Hee Kyung Kim, Woo-Youl Jang, Shin Jung, Ho-Cheol Kang
Pituitary.2021; 24(6): 955. CrossRef - Molecular Pathways in Prolactinomas: Translational and Therapeutic Implications
Betina Biagetti, Rafael Simò
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(20): 11247. CrossRef - A scoping review to understand the indications, effectiveness, and limitations of cabergoline in radiological and biochemical remission of prolactinomas
Rakesh Mishra, SubhasK Konar, Adesh Shrivastava, Pradeep Chouksey, Sumit Raj, Amit Agrawal
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 25(6): 493. CrossRef - Predictors of dopamine agonist resistance in prolactinoma patients
Elle Vermeulen, Jean D’Haens, Tadeusz Stadnik, David Unuane, Kurt Barbe, Vera Van Velthoven, Sven Gläsker
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Dopamine Agonists in Pituitary Adenomas
Erica A. Giraldi, Adriana G. Ioachimescu
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2020; 49(3): 453. CrossRef - Prevalence of Thyroid Disease in Patients Surgically Treated for Pituitary Disease
Kim, Cho, Ku, Jung, Moon, Kim, Shin, Kim, Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(8): 1142. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Response: The Biochemical Prognostic Factors of Subclinical Hypothyroidism (Endocrinol Metab 2014;29:154-62, Myung Won Lee et al.)
-
Myung Won Lee, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(3):402-403. Published online September 25, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.402
-
-
2,628
View
-
24
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Transient high thyroid stimulating hormone and hypothyroidism incidence during follow up of subclinical hypothyroidism
Munir Abu-Helalah, Hussam Ahmad Alshraideh, Sameeh Abdulkareem Al-Sarayreh, AbdelFattah Al-Hader
Endocrine Regulations.2021; 55(4): 204. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- The Biochemical Prognostic Factors of Subclinical Hypothyroidism
-
Myung Won Lee, Dong Yeob Shin, Kwang Joon Kim, Sena Hwang, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(2):154-162. Published online June 26, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.2.154
-
-
3,616
View
-
50
Download
-
14
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
Patients with subclinical hypothyroidism (SHT) are common in clinical practice. However, the clinical significance of SHT, including prognosis, has not been established. Further clarifying SHT will be critical in devising a management plan and treatment guidelines for SHT patients. Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic factors of SHT. MethodsWe reviewed the medical records of Korean patients who visited the endocrinology outpatient clinic of Severance Hospital from January 2008 to September 2012. Newly-diagnosed patients with SHT were selected and reviewed retrospectively. We compared two groups: the SHT maintenance group and the spontaneous improvement group. ResultsThe SHT maintenance group and the spontaneous improvement group had initial thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels that were significantly different (P=0.035). In subanalysis for subjects with TSH levels between 5 to 10 µIU/mL, the spontaneous improvement group showed significantly lower antithyroid peroxidase antibody (anti-TPO-Ab) titer than the SHT maintenance group (P=0.039). Regarding lipid profiles, only triglyceride level, unlike total cholesterol and low density lipoprotein cholesterol, was related to TSH level, which is correlated with the severity of SHT. Diffuse thyroiditis on ultrasonography only contributed to the severity of SHT, not to the prognosis. High sensitivity C-reactive protein and urine iodine excretion, generally regarded as possible prognostic factors, did not show any significant relation with the prognosis and severity of SHT. ConclusionOnly initial TSH level was a definite prognostic factor of SHT. TPO-Ab titer was also a helpful prognostic factor for SHT in cases with mildly elevated TSH. Other than TSH and TPO-Ab, we were unable to validate biochemical prognostic factors in this retrospective study for Korean SHT patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Determinants of Levothyroxine Treatment in Patients with Hypothyroidism
Savaş Karataş, Yalçın Hacıoğlu
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 7(5): 593. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism: Prevalence, Health Impact, and Treatment Landscape
Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 500. CrossRef - Thyroid disorders in Brazil: the contribution of the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil)
I.M. Bensenor
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors for hypothyroidism in euthyroid thyroid nodule patients with lymphocytic thyroiditis on fine needle aspiration cytology
Jeong-Min Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Yejee Lim, Min-Hee Kim, Chan-Kwan Jung, So-Lyung Jung, Moo-Il Kang, Bong-Yun Cha, Dong-Jun Lim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 34(6): 1287. CrossRef - Analysis of the factors affecting the evolution over time of subclinical hypothyroidism in children
Mariella Valenzise, Tommaso Aversa, Giuseppina Zirilli, Giuseppina Salzano, Domenico Corica, Simona Santucci, Filippo De Luca
Italian Journal of Pediatrics.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Reference interval for thyrotropin in a ultrasonography screened Korean population
Mijin Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Soo Han Kim, Yunkyoung Lee, Su-yeon Park, Hyung-don Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Yun Mi Choi, Eun Kyung Jang, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2015; 30(3): 335. CrossRef - Subclinical hypothyroidism: a historical view and shifting prevalence
J. V. Hennessey, R. Espaillat
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2015; 69(7): 771. CrossRef - Letter: The Biochemical Prognostic Factors of Subclinical Hypothyroidism (Endocrinol Metab2014;29:154-62, Myung Won Lee et al.)
Hwa Young Ahn, Yun Jae Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 400. CrossRef - The Biochemical Prognostic Factors of Subclinical Hypothyroidism
You Jin Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(2): 144. CrossRef
- Adrenal gland
- Characteristics of Acromegaly in Korea with a Literature Review
-
Jae Won Hong, Cheol Ryong Ku, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(3):164-168. Published online September 13, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.3.164
-
-
3,674
View
-
50
Download
-
12
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
Acromegaly is a slowly progressive disease caused by excessive growth hormone (GH), which is related to a GH secreting pituitary tumor in most cases. Herein, we describe the epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and treatment of acromegaly in Korea with a literature review. The average annual incidence of acromegaly in Korea was 3.9 cases per million people, which was within the range of previous Western studies. The primary treatment for acromegaly was also transsphenoidal adenomectomy, which accounted for 90.4% of patients whose primary therapeutic options were known. The overall surgical remission rates were 89%, 87%, 64%, 70%, and 50% for modified Hardy classification I, II, IIIA, IIIB, and IV, respectively. An updated and larger study regarding the treatment outcome of medical/radiotherapy in Korean acromegalic patients is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Risk of depression in patients with acromegaly in Korea (2006-2016): a nationwide population-based study
Shinje Moon, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
European Journal of Endocrinology.2023; 189(3): 363. CrossRef - Increased Risk of Hip Fracture in Patients with Acromegaly: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea
Jiwon Kim, Namki Hong, Jimi Choi, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Sin Gon Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 690. CrossRef - Selective screening of patients with associated somatic diseases as a method of early detection of acromegaly
M. B. Antsiferov, V. S. Pronin, T. M. Alekseeva, O. A. Ionova, E. Y. Martynova, Yu. E. Poteshkin, N. A. Chubrova, K. Y. Zherebchikova
Problems of Endocrinology.2021; 67(1): 20. CrossRef - Precision Therapy in Acromegaly Caused by Pituitary Tumors: How Close Is It to Reality?
Cheol Ryong Ku, Vladimir Melnikov, Zhaoyun Zhang, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 206. CrossRef - Patient Characteristics, Diagnostic Delays, Treatment Patterns, Treatment Outcomes, Comorbidities, and Treatment Costs of Acromegaly in China: A Nationwide Study
Xiaopeng Guo, Kailu Wang, Siyue Yu, Lu Gao, Zihao Wang, Huijuan Zhu, Bing Xing, Shuyang Zhang, Dong Dong
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiología de la acromegalia en Ecuador
Enrique López Gavilanez, Kempis Guerrero Franco, Narcisa Solórzano Zambrano, Manuel Navarro Chávez, Camilo López Estrella, Luis Vaca Burbano, Eduardo Marriott Díaz
Endocrinología y Nutrición.2016; 63(7): 333. CrossRef - A magnetic resonance imaging‐based classification system for indication of trans‐sphenoidal hypophysectomy in canine pituitary‐dependent hypercortisolism
A. Sato, T. Teshima, H. Ishino, Y. Harada, T. Yogo, N. Kanno, D. Hasegawa, Y. Hara
Journal of Small Animal Practice.2016; 57(5): 240. CrossRef - Epidemiology of acromegaly in Ecuador
Enrique López Gavilanez, Kempis Guerrero Franco, Narcisa Solórzano Zambrano, Manuel Navarro Chávez, Camilo López Estrella, Luis Vaca Burbano, Eduardo Marriott Díaz
Endocrinología y Nutrición (English Edition).2016; 63(7): 333. CrossRef - An Association Study Between Gene Polymorphisms of Folic Acid Metabolism Enzymes and Biochemical and Hormonal Parameters in Acromegaly
Aslı Tetik Vardarlı, Ayhan Zengi, Vildan Bozok Çetintaş, Muammer Karadeniz, Sadık Tamsel, Ali Şahin Küçükaslan, Timur Köse, Füsun Saygılı, Zuhal Eroglu
Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers.2015; 19(8): 431. CrossRef - Diagnosis, treatment and clinical perspectives of acromegaly
Ferdinand Roelfsema, Gerrit van den Berg
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2015; 10(6): 619. CrossRef - Change in quality of life in patients with acromegaly after treatment with octreotide LAR: first application of AcroQoL in Korea
S. O. Chin, C. H. Chung, Y.-S. Chung, B.-J. Kim, H. Y. Kim, I.-J. Kim, J. G. Kim, M.-S. Kim, S.-Y. Kim, E. J. Lee, K. Y. Lee, S.-W. Kim
BMJ Open.2015; 5(6): e006898. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef
- A Case of Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults Developed after Surgical Cure of Growth Hormone Secreting Pituitary Tumor.
-
Wonjin Kim, Jung Ho Kim, Youngsook Kim, Ji Hye Huh, Su Jin Lee, Mi Sung Park, Eun Yeong Choe, Jeong Kyung Park, Myung Won Lee, Jae Won Hong, Byung Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Hyun Chul Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(4):318-322. Published online December 20, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.4.318
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Acromegaly is generally caused by a benign growth hormone (GH)-secreting pituitary adenoma. It is characterized by a wide range of complications; cardiovascular, respiratory, bone and joint, and metabolic complications. Among them, impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes mellitus, due to GH-induced insulin resistance, has been reported in approximately 16-46% and 19-56%. They are usually improved following the treatment of acromegaly, surgical or medical therapy. We report a first case of 36-year-old man who was paradoxically diagnosed with GAD antibody positive latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) after the surgical cure of acromegaly.
- A Case of Pituitary Adenoma with Simultaneous Secretion of TSH and GH.
-
Eun Young Lee, Cheol Ryong Ku, Hyun Min Kim, Woo Kyoung Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Sena Hwang, Do Hwan Kim, Dong Yeob Shin, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(2):160-165. Published online June 1, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.2.160
-
-
2,967
View
-
30
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Thyrotropin (TSH)-secreting pituitary adenoma is a very rare disease. In one-quarter of patients suffering from this disease, the pituitary tumor secretes other anterior pituitary hormones. Herein, we report a case of pituitary adenoma with simultaneous secretion of TSH and growth hormone (GH). A 34-year-old female visitied local hospital complaining of sweating, intermittent palpitation, and weight loss of 8 kg within 1 year. The patient had undergone trans-sphenoidal surgery 3 years prior for resolution of a TSH and GH co-secreting pituitary adenoma. She had been administered somatostatin analogue prior to visiting our hospital. The patient's GH levels were suppressed to below 1 ng/mL on the 75 g oral glucose tolerance test, and her basal insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) level was within normal range. Thyroid function tests demonstrated increased levels of both free thyroxine and TSH. Sella-MRI revealed pituitary adenoma at the floor of the pituitary fossa, approximately 2 cm in height. Therefore, she was diagnosed with residual TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma. The patient again underwent trans-sphenoidal surgery and entered complete remission, based on hormone levels and MRI findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery of Pituitary Adenomas: Preliminary Results of the Neurosurgery Service of Hospital Cristo Redentor
Gerson Perondi, Afonso Mariante, Fernando Azambuja, Gabriel Frizon Greggianin, Wanderson William dos Santos Dias, Giulia Pinzetta
Arquivos Brasileiros de Neurocirurgia: Brazilian Neurosurgery.2023; 42(02): e89. CrossRef - A case of a co-secreting TSH and growth hormone pituitary adenoma presenting with a thyroid nodule
Laura Hamilton Adams, Derick Adams
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism Case Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Correlation between Pituitary Insufficiency and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding in Non-Functioning Pituitary Adenomas.
-
Hyun Min Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Young Lee, Woo Kyung Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Sena Hwang, Mi Jung Lee, Seung Ku Lee, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(4):310-315. Published online December 1, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.4.310
-
-
2,035
View
-
28
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Non-functioning pituitary adenomas (NFPAs) are characterized by the absence of clinical and biochemical evidence of pituitary hormone hypersecretion, and these tumors constitute approximately one third of all the tumors of the anterior pituitary. Recently, hormonal deficiencies have gradually evolved to become the leading presenting signs and symptoms in patients with NFPAs. We investigated pituitary hormonal insufficiencies according to the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings in patients with NFPA. METHODS: We evaluated the patients who were newly diagnosed with NFPA from 1997 through 2009. Among them, we analyzed 387 patients who were tested for their combined pituitary function and who underwent MRI. The severity of the hypopituitarism was determined by the number of deficient axes of the pituitary hormones. On the MRI study, the maximal diameter of the tumor, Hardy's classification, the thickness of the pituitary gland and the presence of stalk compression were evaluated. RESULTS: The mean age was 46.85 +/- 12.93 years (range: 15-86) and 186 patients (48.1%) were male. As assessed on MRI, the tumor diameter was 27.87 +/- 9.93 mm, the thickness of the normal pituitary gland was 1.42 +/- 2.07 mm and stalk compression was observed in 201 patients (51.9%). Hypopituitarism was observed in 333 patients (86.0%). Deficiency for each pituitary hormone was most severe in the patients with Hardy type IIIA. Hypopituitarism was severe in the older age patients (P = 0.001) and the patients with a bigger tumor size (P < 0.001) and the presence of stalk compression (P < 0.001). However, the patients who had a thicker pituitary gland showed less severe hypopituitarism (P < 0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that age, tumor diameter and the thickness of pituitary gland were important determinants for pituitary deficiency (P = 0.004, P < 0.001, P = 0.022, respectively). CONCLUSION: The results suggest that the hormonal deficiencies in patient with NFPA were correlated with the MRI findings, and especially the tumor diameter and preservation of the pituitary gland.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinical Parameters to Distinguish Silent Corticotroph Adenomas from Other Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas
Daham Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Se Hee Park, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
World Neurosurgery.2018; 115: e464. CrossRef
- Secondary Pituitary Hyperplasia Induced by Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Related Hypothyroidism: A Case Report.
-
Kwang Joon Kim, Hyun min Kim, Obin Kwon, Eun Young Park, Yong ho Lee, Jae Won Hong, Jin Wi, Eun Jig Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2010;25(1):72-77. Published online March 1, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2010.25.1.72
-
-
1,949
View
-
33
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Pituitary hyperplasia associated with untreated primary hypothyroidism in children is a rare condition. There are only a few reports on this condition in children, and especially when pituitary hyperplasia is accompanied with Hashimoto thyroiditis and growth arrest. Here, we describe an unusual association of pituitary hyperplasia with hypothyroidism and growth retardation, and this was all caused by Hashimoto thyroiditis. Hormonal testing showed a low thyroxine level and a high thyroid stimulating hormone level, elevated anti-thyroglobulin, low growth hormone levels and prepubertal levels of gonadotropins. A large intrasellar mass expanding beyond the sella turcica was detected on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Homogeneous contrast enhancement of mass highly suggested that it was a pituitary hyperplasia rather than a pituitary tumor. Therapy with L-thyroxine resulted in rapid improvement of the clinical signs, including renewed growth, normalization of the hormone levels and resolution of the pituitary hyperplasia on MRI within 90 days. In children, prolonged unrecognized primary hypothyroidism might be accompanied by growth deficiency and pubertal disharmony. Physicians must be aware of pituitary hyperplasia in these cases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Pituitary macroadenoma secondary to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: inadvertent diagnosis in a pre-pubertal girl
Deepanjan Bhattacharya, Rakesh Kumar, Jaivinder Yadav
Tropical Doctor.2020; 50(3): 240. CrossRef - Pituitary Hyperplasia Secondary to Hypothyroidism Caused by Hashimoto's Thyroiditis in a Female Adolescent
Jeoung Suk Kim, Min Sun Kim, Sun Jun Kim, Gyung Ho Chung, Pyoung Han Hwang, Dae-Yeol Lee
Journal of Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology.2011; 16(3): 185. CrossRef
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Octreotide Long-acting Repeatable and Lanreotide Autogel in Acromegalic Patients.
-
Jeong Kyung Park, Eun Jig Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2010;25(1):25-27. Published online March 1, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2010.25.1.25
-
-
1,501
View
-
25
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Medical Treatment with Somatostatin Analogues in Acromegaly: Position Statement
Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Byung Joon Kim, Sung-Woon Kim, Kyeong Hye Park, Kee Ho Song, Seungjoon Oh, Hyun Koo Yoon, Eun Jig Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Dong
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2019; 94(6): 485. CrossRef
- A Case of Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome in a Patient with Partial Hypopituitarism.
-
Obin Kwon, Eun Young Park, Jin Young Yoon, Kwang Joon Kim, Yong ho Lee, Jae Won Hong, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong Soo Cha
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(4):281-286. Published online December 1, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.4.281
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Insulin autoimmune syndrome is one of the rare causes of hypoglycemia, and characterized by hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia associated with high titer of antibodies to endogenous insulin. We report a case of insulin autoimmune syndrome in a 57-year-old woman, presenting with mental changes due to hypoglycemia. She had no history of diabetes or insulin administration. The serum C-peptide level was 4.69 ng/mL and the insulin concentration was 229.55 microU/mL, when fasting plasma glucose level was 32 mg/dL. The insulin-to-glucose ratio was 7.17, while there was no radiologic evidence of insulinoma. The insulin antibody level was over 100 microU/mL, resulting in the diagnosis of insulin autoimmune syndrome. Hormonal studies revealed partial hypopituitarism and a lack of glucagon-response to hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia disappeared with replacement of prednisolone with levothyroxine therapy. Under secretion of growth hormone and of adrenocorticotropic hormone due to hypopituitarism were associated with insufficient counterregulation to hypoglycemia. One should keep in mind that insulin autoimmune syndrome or hypopituitarism is one cause of hypoglycemia in patients with no history of diabetes, and corticosteroid can be an effective treatment for both diseases.
- A Case of Graves' Disease Presenting with Chorea.
-
Cheol Ryong Ku, Hyung Jun Park, Sung Jin Hong, Dong Yeob Shin, Jin Ha Lee, Moon Jae Chung, Mi Ae Cho, Tae Woong Noh, Byung In Lee, Eun Jig Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(5):342-346. Published online October 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.5.342
-
-
1,988
View
-
20
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hyperthyroidism is invariably accompanied by nervous system dysfunction. Specifically, irritability, emotional lability, and hyperkinesia are the signs and symptoms most frequently observed. In rare instances, chorea and/or choreoathetosis are associated with hyperthyroidism. Full evaluation for the etiology of chorea is necessary prior to initiating treatment. We recently encountered a 42-year-old female who initially presented with hyperthyroidism and showed subsequent development of progressive generalized chorea. The patient was diagnosed with chorea secondary to Graves' disease after exclusion of other causes of chorea and improved after the initiation of pulse administration of intravenous methylprednisolone sodium succinate (Solu-medrol(R), 1000 mg for 5 days) and oral antithyroid medication. This treatment strategy resulted in the resolution of involuntary movements. The steroid administration was eventually tapered, and the patient has been maintained on antithyroid and steroid therapy with considerable success since the initiation of treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Unilateral upper limb chorea associated with hyperthyroidism: A case report and literature review
Wei Chen, Bin Wu, Hongna An, Kaiying Zheng, Daming Zhai, Jiahua Zang, Xiaobing Wu
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-Thyroid Peroxidase/Anti-Thyroglobulin Antibody-Related Neurologic Disorder Responsive to Steroids Presenting with Pure Acute Onset Chorea
Ritwik Ghosh, Subhankar Chatterjee, Souvik Dubey, Alak Pandit, Biman Kanti Ray, Julián Benito-León
Tremor and Other Hyperkinetic Movements.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Non-functional Pituitary Adenoma Detected on (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography ((18)F-FDG-PET) in a Patient with Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma.
-
Jin Ha Lee, Seung Jin Han, Se Eun Park, Mi Ae Cho, June Won Cheong, Mijin Yun, Yumie Rhee, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(2):137-141. Published online April 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.2.137
-
-
1,814
View
-
19
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the modality of choice for the detection and characterization of a pituitary adenoma. Uptake of (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) by intrasellar tumors, including pituitary adenomas, has been reported in several previous studies. We report a case where a pituitary adenoma was detected on FDG-positron emission tomography (PET), but the tumor was not detected with the use of sellar MRI. A 31-year-old woman was referred to the clinic due to a focal increase of FDG uptake at the pituitary fossa seen on whole body FDG-PET. The patient was receiving chemotherapy due to a recurred B-cell lymphoma of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type. Subsequently, sellar MRI was performed, and images showed a small non-enhancing heterogenous cystic lesion in the midline of the pituitary gland, radiologically suggestive of a Rathke's cleft cyst. However, sellar MRI failed to identify a lesion consistent with a pituitary tumor that corresponded to the site of increased FDG uptake detected by the use of PET, despite the inclusion of a dynamic contrast enhanced sequence. Despite the negative findings of the MRI examination, basal and stimulated levels of the GnRH free alpha-subunit were profoundly increased. Therefore, we suspected the presence of a non-functional pituitary tumor in addition to a Rathke's cleft cyst, rather than pituitary involvement of a lymphoma, based on the hormone levels and PET scan findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinical Characteristics of 16 Patients with Pituitary Tumor Incidentally Detected by18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET-CT (18F-FDG PET-CT)
Hyung Jin Kim, Gi Jeong Cheon, A Ra Cho, Chang Hoon Lee, Sang Min Youn, Se jin Ahn, Sang Eon Jang, Jung Min Kim, Yun Yong Lee, Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2010; 25(4): 321. CrossRef
- The Characteristics and Follow-up of Pituitary Incidentaloma.
-
Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(2):109-110. Published online April 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.2.109
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- A Case of Turner's Syndrome with Transient Hypopituitarism.
-
Ji Sun Nam, Min Ho Cho, Jung Min Roh, Hai Jin Kim, Ji Eun Yoon, Han Young Jung, Jong Suk Park, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(4):266-271. Published online August 1, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.4.266
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Turner's syndrome is characterized by short stature and gonadal dysgenesis, and it is often associated with various systemic manifestations, such as cardiovascular, renal, thyroidal, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal disorders. Though very rare, it can also be accompanied by hypopituitarism. It is important to give a meticulous medical attention to short females with gonadal dysgenesis so that neither disease is neglected or gets delayed diagnosis. In this case, Turner's syndrome and hypopituitarism were diagnosed almost simultaneously, but hypopiuitarism was transient, and the normal pituitary function was recovered spontaneously without any treatment. Initial sella MRI showed mild congenital hypoplastic hypopituitarism, and combined pituitary function test was compatible with hypopituitarism, but after 5 years, though growth hormone deficiency was still present, otherwise normal pituitary function was noted without any change in MRI. Herein, we are reporting a case of Turner's syndrome with transient idiopathic hypopituitarism with the review of literature.
- A Case of Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia Coexisting with Low Bone Mass.
-
Sung Wan Chun, Se Hwa Kim, Jong Yul Jung, Won Na Suh, Ji Ae Moon, Jong In Yook, Yoon Sok Chung, Yumie Rhee, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(6):583-588. Published online December 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.6.583
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia is caused by heterozygous loss-of-function mutation of the calcium sensing receptor gene, and this is characterized by mild, persistently elevated levels of serum calcium without symptoms or complications. We present a case of clinically diagnosed familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia with unexpected low bone mass. A 19-year-old man presented with incidentally discovered hypercalcemia. He showed normal growth and sexual maturation. Biochemical studies showed hypercalcemia, increased parathyroid hormone, hypocalciuria, a decreased urinary calcium-creatinine ratio and decreased serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D. The other hormonal studies were normal. Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry showed low bone mineral density, and the Sestamibi scan showed no abnormality in the parathyroid glands. Iliac bone biopsy showed a general decrease in bone density and increased porosity of the cortical bone. Normal mineralization was also shown, but in part, osteoid deposition was also found. Direct sequencing of the patient's calcium sensing receptor gene showed a point mutation at exon7, Q926R.
- A Case of Autoimmune Hypoglycemia due to Insulin Antibody in Patient with End Stage Renal Disease.
-
Ji Ye Jung, Eun Seok Kang, Beom Seok Kim, Sung Wan Chun, Yumie Rhee, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(6):536-541. Published online December 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.6.536
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Fasting hypoglycemia results from several mechanisms. Autoimmune hypoglycemia is one of the rare causes of hypoglycemia, and characterized by hyperinsulinemia, fasting hypoglycemia and the presence of autoantibodies to insulin or insulin receptor. We report here on a 64-year-old male patient with autoimmune hypoglycemia with end stage renal disease. He had no history of diabetes or insulin use. He had experienced several severe hypoglycemic events. The serum C-peptide level was 7.48 ng/mL and the insulin concentration was 115.4 micro U/mL when the fasting plasma glucose level was 88 mg/dL. The insulin to glucose ratio was 5.42, which suggested the presence of insulinoma. Yet the radiologic studies, including magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, endoscopic ultrasonography and selective calcium stimulated venous sampling revealed no evidence of insulinoma. The insulin autoantibody level was 62 micro U/mL. Therefore, we could diagnosis the autoimmune hypoglycemia. The hypoglycemia was treated with prednisolone and the patient recovered from this. His insulin level decreased to 21.11 micro U/mL and the insulin autoantibody level decreased to 34 micro U/mL. Hypoglycemia in the hemodialysis patients is not uncommon. One should bear in mind autoimmune hypoglycemia as one of the causes of hypoglycemia in patients with no history of diabetes.
- Evaluation and Treatment of Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency: An American Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline.
-
Sung Woon Kim, Yoon Sok Chung, Eun Jig Lee, Seong Yeon Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(6):460-475. Published online December 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.6.460
-
-
1,856
View
-
23
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Reassessment of GH Status and GH Therapy in Adults with Childhood-onset GHD: Transitional Care from Adolescence to Adulthood
Jin-Ho Choi, Han-Wook Yoo
Journal of Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology.2011; 16(1): 1. CrossRef
- Endocrine Regeneration Therapy using Adenoviral vector.
-
Eun Jig Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(4):301-305. Published online August 1, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.4.301
-
-
1,366
View
-
16
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No Abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of Various Types of Distribution on Probabilistic Method and FAD
Ouk Sub Lee, Dong Hyeok Kim
Key Engineering Materials.2007; 353-358: 2561. CrossRef
- Mutations in Thyroid Hormone Receptor-beta Associated with Patients with Generalized Resistance and Pituitary Resistance to Thyroid Hormone.
-
Yong Seok Yun, Sung Kkwan Hong, Chul Woo Ahn, Jae Hyun Nam, Seok Won Park, Bong Su Cha, Young Duk Song, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2000;15(1):113-120. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- We report a point mutation in the TRbeta gene in korean patients with generalized resistance and pituitary resistance to thyroid hormone. One mutation at TRbeta (P453S) were detected in patient with pituitary resistance to thyroid, which showed different phenotype, generalized resistance to thyroid hormone, in her mothers. But, the other (C31Y), did not show clear relations with the disease. Therefore, further study of molecular and cellular basis will be warranted to explain the clear mechanism of the resistance to thyroid hormone.
- Clinical use of Urinary Androgen Metabolites in Hyperprolactinemia.
-
Kyoung Rae Kim, Sung Kil Lim, Young Duk Song, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Eun Sook Kim, Su Youn Nam, Eun Jig Lee, Bong Chul Jung, Byeong Kee Choi, Jae Ho Shin
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1997;12(3):443-449. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Hyperprolactinemia has been linked with hyperandrogenism and hirsutism in some women. High plasma Dihydroandrosterone and DHA-S levels were reported in patients with hyperprolactinemia and a dissociation of adrenal androgen and cortisol secretion occurs in normal subjects. The mechanism has not been elucidated, but it has been suggested that pituitary factors other than ACTH modulate adrenal androgen synthesis, One candidate hormone is prolactin. Adrenal tissue has been found to possess prolactin receptors and prolactin has been shown to act synergistically with ACTH and lowers the activity of the enzyme 5a-reductase or 3B-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3B-HSD). The aim of this study was to investigate the secretion of adrenal androgen metabolites in patients with idiopathic hyperprolactinemia and prolactinoma and to deterrnine the relationship with prolactin and androgens. METHODS: We measured 24 hour-urinary DHEA, androstenedione, androsterone, pregnenolone, tetrahydrocorticoid and cortisol in 16 normal controls and 5 patients with idiopathic hyperprolac-tinemia (HP) and 12 patients with prolactonoma in the early follicular phase. RESULTS: Urinary DHEA, AD (androsteredione), and androsterone, the metabolites of adrenal androgen, were significantly higher in both patients with idiopathic HP and prolactinoma compared with those in normal controls (p<0.05), whereas they were not different in both disease groups. Urinary pregnenolone levels, early metabolite of adrenal steroid synthesis, were lower in patients. In contrast, urinary tetrahydorcortisol and cortisol were higher in patients compared to controls. There was no difference in DHEA:androsterone ratio between patients and controls. And there were no correlation between prolactin levels and the levels of androgenic metabolites or clinical symptoms. CONCLUSION: Prolactin has a tropic effct on the secretion of androgens and steroids by the adrenal cortex. But prolactin levels were not correlated with androgen levels or clinical symptoms (amenorrhea), and it might have little effect on lowering the activity of 3B-HSD.
- Primary empty sella syndrome.
-
Kyoung Rae Kim, Sung Kil Lim, Young Duk Song, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Eun Sook Kim, In Jai Kim, Yoon Jae Moon, Sang Kyu Na, Su Youn Nam, Eun Jig Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1997;12(3):386-392. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Primary empty sella syndrome (PES) is thought to arise from an incompetent diaphragma allowing progressive herniation of arachnoid membrane with secondary compression and atrophy of the pituitary gland. As a consequence of the improvement and widespread use of neuroradiological techniques, such as computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), empty sella is more frequently disclosed. The aim of this study is to assess the associated clinical characteristics and endocrinologic disturbance in empty sella syndrome. METHODS: From January 1986 to June 1996, 171 patients with empty sella syndrome have undergone analysis for clinical characteristics and associated disease. RESULT: In our study, PES was diagnosed in 131 of the 171 patients (77%). Primary empty sella syndrome was frequent in middle aged women (female:male 115:16, mean age: 50.6+12.6 years). The common clinical features were headache (80.2%), obesity (72.5%), and hypertension (27.5%). Most of patients with PES have normal pituitary function (75%). The frequent pituitary dysfunction was hyperprolactinemia in PES (21%). Partial and total emptiness of sella on sella CT or MRI were in 111 (84.7%) patients, and in 20 (15.4%) patients, respectively. The most common associated disease with empty sella syndrome was pituitary adenoma. CONCLUSION: PES should be considered as a possible cause in obese middle aged women with unexplained headache. The combined pituitary function test should be considered for evaluation of pituitary dysfunction when clinically suspected.
- Clinical and Sellar MR Findings in Central Diabets Inspidus.
-
Bong Soo Cha, Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Su Youn Nam, Eun Jig Lee, Sei Chang Oh, Byung Hee Lee, Dong Ik Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(3):285-292. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
s: Diabetes insipidus(DI) is a clinical syndrome characterized by excretion of copious volumes of dilute urine combined with persistent intake of abnormally large quantities of fluid. Central DI, caused by lack of antidiuretic hormone(ADH), most often results from lesions in the hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal axis. Magnetic resonance(MR) imaging is particularly useful in documenting the presence of a structural lesion, as opposed to assigning a diagnosis of idiopathic DI for which only symptomatic therapy is prescribed. Recently, several reports have described a specific MR finding in central DI, that is absence of normal posterior pituitary bright spot(PPBS). Methods: We retrospectivesly studied the clinical and MR findings in 25 patients with central DI, diagnosed by warter deprivation test. Results: 1) The subjects included 17 males and 8 females, between the ages of 2 and 58 years. 2) 24-hour urine volumes were 2,340~13,750 mL, and mean urine osmolarity was 147.7±65.8 mOsm/kg. The 23 subjects diagnosed complete central DI by warter deprivation test. 3) We found that the most common cause of cntral DI was infiltrative lesions of hypothalmic-neurohypophyseal axis(60%). Germ cell tumor was the single leading cause in present study, accounting for 36% of cases. The other causes were found, including pituitary apoplexy, meningitis, and trauma. Idiopathic central DI accounted for 20% of all cases. 4) Growth hormone deficiency was the most common accompanying anterior pituitary deficit, and panhypopituitarism was found in 7 cases, Hyperprolactinernia was seen in 6 cases. 5) In all patients, PPBS on Tl weighted MR images were not observed. A thickened pituitary stalk was seen in 15 cases(9 patients with germ cell tumor, 3 patients with histiocytosis X, 1 patient with tuberculosis, 2 patients with unknown origin). Conclusion: In our results, the most common causes of central DI was suprasellar infiltrative lesions. MR is currently the imaging methods of choice in the evaulation of dysfunction of the hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal system in patients with central DI. A specific MR finding, that is loss of normal PPBS allows a confirmative diagnosis of central DI.
- Reduction of Central Dopamine Release in Hyperprolactinemia.
-
Bong Soo Cha, Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Su Youn Nam, Eun Jig Lee, Bong Chul Chung, Jung Han Kim, Sei Chang Oh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(3):277-284. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
Prolactin(PRL) secretion is tonically inhibited by doparnine that originates from the hypothalamic tuberoinfundibular tract and reaches the lactotroph via the hypophyseal portal vessel. Hyperprolactinemia associated with oligomenorrhea-amenorrhea, galactorrhea and/or infertility is mainly due to PRL-secreting pituitary adenoma(PA). The diagnosis of idiopathic hyperprolac- tinemia(IHP) is made, when hyperprolactinemia is sustained and all causes of hyperprolactinemia are excluded without radiological abnormality. It is not known, whether IHP and PA are two distinct entities or two subsequent phases of the same disease. The etiology of both disorders remains unresolved. We investigated that PRL hypersecretion in patients with IHP and PA may be the result of a defect in the central nervous system(CNS)-dopamine release, and that there may be some differences in pathogenesis of both diseases. Methods: We measured 24 hour-urinary dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and serum and 24 hour-urinary VMA(vanillyl rnandelic acid), HVA(homovanilic acid), DOPAC(3,4-dihydroxy phenylaceticacid), MHPG(3-methoxy 4-hydroxy phenylglycol) in 10 normal controls, 9 patients with IHP, and 17 patients with PA in the early follicular phase. Results: Urinary HVA and DOPAC concentrations, the major metabolites of CNS dopaminergic activity, were signficantly lower in both patients with IHP and PA compared with those in normal controls(p 0.05), whereas they were not different in both disease groups. Dopamine, norepine-phrine, epinephrine, MHPG concentrations were similar to those of the normal controls. Although VMA concentrations of both disease groups were significantly higher than those of normal controls, all of them were within normal range. Conelusion: Although our data are unable to establish the precise biochemical defect responsible for central dopamine deficiency in pathogensis of IHP and PA, we can support the presence of a pathological reduction of brain dopamine activity in IHP and PA.
- A Case of Anterior Cervical Lipoma Mimicking Diffuse Goiter.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Su Youn Nam, Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Kyung Rae Kim, Jun Sik Na, Yee Hyun Nam, Jeon Hong Kang, Jung Ki Seo
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(4):418-423. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Lipoma is a benign fatty tumor that can arise in any location of the body where fat is present. It is found most commonly in the upper half of the body, particularly the head and neck, shoulders, and back. A mass in the antero-inferior part of the neck may be initially thought to be thyroid masses and then other cervical masses should be considered. Ultrasongraphic examination of benign lipoma demonstrates solid and echogenic mass and may differentiate nonthyroid from thyroid masses. Although the location of tumors, its consistency, and its motion with deglutition, seperation from the thyroid on sonographic examination, all pointed to nonthyroidal origin, did not rule out a possible mass that isolated from the lobes of the thyroid. Fine needle aspiration and biopsy can provide clear answer.We herein report a case of anterior cervical mass in a 48-yr-old male patient presenting a non-tender, slightly hard and nodular mass slowly growing for several years and moved with swallowing, and diagnosed his case as benign lipoma using thyroid scan and ultrasonography. When we encounter patients with anterior neck mass, we should consider benign lipoma mimicking diffuse goiter.
- Clinical and Endocrinologic Differences between Prolactinoma and Pseudoprolactinoma Proven by Immunohistochemical Study.
-
Jae Wha Jo, Eun Jig Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Su Youn Nam, Young Duk Song, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Tae Seung Kim, Sun Ho Kim, Kyung Rae Kim, Bong Soo Cha, Ji Hyun Lee, Sung Kil Lim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(4):362-369. Published online November 7, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hyperprolactinemia is the most common hypothalamo-pituitary disorder encountered in clinical endocrinology. Excluding the drug-induced hyperprolactinemia, the most common cause of this disorder is a pituitary tumor. Prolactinoma is mainly made up of prolactin-secreting cells but pseudoprolactinoma is tumor that does not secrete prolactin itself. The pseudoprolactinoma interrupts the flow of prolactin inhibiting factor, dopamine, from the hypothalamus through the pituitary stalk to the normal pituitary. The differentiation prolactinoma from pseudoprolactinoma is vitally important since true prolactinomas are most commonly responded well in terms of tumor shrinkage to medical treatment using dopamine agonist therapy, whereas pseudoprolactinomas do not. Thus surgical treatment is clearly indicated as first-line treatment if we know that a lesion is a pseudoprolactinoma. We compared prolactinoma with pseudoprolactinoma in clinical and endocrinologic characteristics of 48 cases after immunohistochemical diagnosis. We could not find any differential point of both tumors in clinical and radiological characteristics although some differences were exist. But we had found the relationship between the mean level of pretreatment serum prolactin and the presence of positive immunohistochemical stain for prolactin. The pretreatment serum prolactin level was significantly higher in patients with tumors showing many prolactin immunohistochemical staining cells than in those with none(p<0.05). When the pretreatment serum prolactin exceeded 100ng/ml, the tumors contain 94% of prolactin positive cells in stain. So, if the pretreatment serum prolactin exceeds 100ng/ml, we primarily suspect prolactinoma and medical treatment should be considered. If the pretreatment level below 100ng/ml, we suspect pseudoprolactinoma and surgical treatment should be considered.
- Immunohistochemical Study of c - Myc, c - Fos and c - Jun Oncoprotein Expression in the Human Pheochromocytoma.
-
Jae Wha Jo, Eun Jig Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Kyung Rae Kim, Su Youn Nam, Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Yong Hye Lee, Tae Seung Kim, Kwan Woo Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(1):26-34. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A large number of studies for genes involved in oncogenesis have been done during last decade. Over 20 oncogenes have been isolated characterized, and the oncogene expressions in human tumors have been examined. The proto-oncogenes of c-Myc, c-Fos and c-Jun, which modulate the transcription factors, have overexpressed in a variety of human cancers. Immunohistochemical method was used in this study to examine c-Myc, c-Fos and c-Jun oncoprotein expression in 31 patients with human pheochromocytoma 28(90.0%) were benign and 3(10.0%) malignant. C-Myc oncoprotein immunoreactivity was found in 24 cases(77.4%), c-Fos in 29(93.5%), and c-Jun in 25(80.6%). Twenty-one(67.7%) showed positive immunoreactivity for all these oncoproteins, six(19.4%) for 2 oncoproteins, 3 for one oncoprotein. Only 1 case showed negative immunoreactivity for all 3 oncoproteins. The oncoprotein immunoreactivity did not correlate with the amount of 24 hour urinary catecholamine excretion. Although the number of malignant pheochromocytomsa was not so many, most of them showed that the immunoreactivity for oncoprotein was more than 30 percent of tumor cells.The expression of c-Myc, c-Fos and c-Jun oncoprotein were frequently found in human pheochromocytoma. These results suggest that the oncoprotein expression may play an important role in tumorogenesis and proliferation of human pheochromocytoma.
- A Case of Giant Cell Granuloma of The Pituitary Gland.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Tae Seung Kim, Sun Ho Kim, Bong Soo Cha, Dong Hun Choi, Jeong Il Jeong
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(3):284-288. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Granulomatous disease of the pituitary gland are uncommon disorders which are rarely diagnosed in patients presenting for hypophysectomy. The majority of reported cases come from neuropsy material and include infectious and systemic disease such as tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, syphilis and fungal infections. We experienced giant cell granuloma of the pituitary gland in a 47 years-old woman. The patient suffered from headache, polyuria and polydipsia. MR images of brain demonstrated a hyposignaled mass. The fibrous tissues were removed by transsphenoidal approach. The clinical and histopathological features of this rare entity are reviewed.
- Complication and Prognosis of Craniopharyngioma According to the Age of Onset.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Kyung Rae Kim, Kun Hoon Song, Bong Soo Cha, Ji Hyun Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(3):262-272. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Craniopharyngioma is the most common tumor involving the hypothalamo-pituitary area in childhood and adolescence. Recently, we carried out collective review of 70 patients with craniopharyngioma treated from January 1980 to December 1994 in order to inverstigate the endocrine outcome and survival according to the age of onset.The following results were obtained:1) The male to female ratio was 1:1. Age at diagnosis ranged from 2 to 64 years(mean age: 23) with the greatest frequency in the 2nd decade of life(28.6%). Of the 70 cases, the first group, 27 cases were under the age of 15, and the other group, 43 cases were over 15 year-old.2) The most common symptom at diagnosis in both groups was headache. In the adult group, symptoms related to hypogonadism(amenorrhea, decreased libido, galactorrhea etc.) were not uncommon. The lag of time between onset of symptom and hospital visit ranged from 3 days to 156 months(mean: 20 months).3) The main site of tumor was suprasellar region in both groups. The most common CT finding in both groups was calcification in sella turcica.4) In pre-operative combined pituitary function test, the most common, abnormal responses were shown in growth hormone and thyroid stimulating hormone in both groups. In addition, prolactin frequently showed abnormal response in the adult group.In post-operative combined pituitary function test, more hormones tended to reveal abnormal response in the group treated with surgery plus radiation therapy.5) The operation by subtotal removal followed by radiation therapy was the most commonly used method in treatment of both groups. After treatment, panhypopituitarism was occurred more frequently in the group treated with RT after surgery than those treated with surgery alone, but the difference was not statistically significant(p=0.136 in childhood, 0.436 in adults). Except the cases with panhypopituitarism, the most commonly encountered endocrine abnormalities were growth retardation in the children group, and hypogonadism in adult. The recurrence was clinically observed in 11 cases. The recurrence rate were 11.1% in children, and 18.6% in adult respectively. The mean time from the initial treatment to recurrence was 23 months. There was no significant difference in recurrence rate between the group treated with RT after subtotal removal and the group treated with total removal(p=0.475).The overall five-year survival rate after treatment was 82.8%. According to the treatment modalities, the patients undergone RT after subtotal removal survived much longer than those treated with other modalities such as subtotal removal only or total removal, but the differences in survival were not statistically significant(Log rank test, p=0.0539).
- The Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor - α on Extra Thyroidal Conversion of T4 to T3 in Slices and Extracts of Porcine Liver and Kidney.
-
Jae Wha Jo, Moon Suk Nam, Su Youn Nam, Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Kyung Rae Kim, Eun Jig Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(3):242-248. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abnormal thyroid function is seen in a wide variety of patients with acute and chronic nonthyroidal-illness, consisting of reduction in both thyroid function and peripheral T_4 to T_3 conversion including decreased serum thyroxin(T_4), decreased triiodothyronine and normal or slightly increased serum TSH. Recently increasing awareness of the role tumor necrosis factor-alpha(TNF-alpha) in systemic illness led us to consider a possible contribution of TNF-alpha to thyroid dysfunction in this setting. So we hypothesized that TNF-alpha might affect peripheral conversion of T_4 to T_3. We, therefore, explored the effects of TNF-alpha in slices and extracts of porcine liver and kidney. Thyroxine(T_4, 5ug/ml) was incubated in 0.15M phosphate buffer(PH 7.4) with slices(approximately 0.3 g-equivalent of tissue) and extracts(approximately 0.23 g-equivalent of tissue) of porcine liver and kidney with various concentrations(0-500pg/ml) of recombinant human TNF-alpha for 2 hours at 37 degree, and the T_3 generated during incubation was measured by radioimmunoassay of an ethanol extracts of the extracts and the homogenates of the slices. The slices produced more T_3 than extracts and the kidney was more active than the liver. TNF-alpha inhibited T_4 to T_3 conversion in dose-dependent manner in slices and extracts of porcine liver and kidney. Our data suggest that TNF-alpha have inhibitory effect of T_4 to T_3 conversion in liver and kidney(J Kor Soc Endocrinol 10: 242-248, 1995).
- The Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor - α on the Thyroglobulin Synthesis and TSH Action in Cultured Porcine Thyroid Cells.
-
Jae Wha Jo, Eun Jig Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Su Youn Nam, Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Kyung Rae Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(3):220-228. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abnormal thyroid function is seen in a wide variety of patients with acute and chronic nonthyroidal-illness, consisting of reduction in both thyroid function and peripheral T_4 to T_3 conversion including decreased serum thyroxin(T_4), decreased triiodothyronine and normal or slightly increased serum TSH. Recently increasing awareness of the role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha(TNF-alpha) in systemic illness led us to consider a possible contribution of TNF-alpha to thyroid dysfunction in this setting. So we hypothesized that TNF-alpha might affect the function of the thyroid gland. We, therefore, explored the effects of TNF-alpha on the cultured porcine thyroid cells in TSH-stimulated and TSH-nonstimulated conditions. Primarily cultured porcine thyroid cells were incubated with various concentrations(-500pg/ml) of recombinant buman TNF-alpha and bTSH(1mu/ml), with measurement of secreted thyroglobulin(Tg) and cyclic AMP(c-AMP) as the end points of stimulation, and produced intracellular Tg by pulse-labelling. TNF-alpha significantly inhibited TSH-stimulated intracellular Tg synthesis and extracellar Tg secretion at 200 and 500pg/ml concentration. TNF-alpha didn't affect c-AMP production at any concentration tested. So we conclude that increased in serum TNF-alpha may be responsible for reduced thyroid function in patients with acute and chronic nonthyroidal-illness.
- 10 Years Prospective Study for the Surgical Total Removal of Pituitary Tumor; Preliminary Report - 2, 5 Years Follow Up.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Kap Bum Huh, Sun Ho Kim, Dong Ik Kim, Byung Hee Lee, Ju Heon Yoon, Su Yeon Choi, Joong Uhn Choi, Sang Seop Chung, Kyu Chang Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(2):85-94. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The goal of the pituitary tumor surgery is restoration of the normal endocrine function and releaving the pressure effects of the tumor mass on the adjacent neural structures. The authors had proceeded with the 10 years prospective follow-up study for the endocrine function and recurrence of pituitary tumor in the patients who received the complete total resection of tumor mass by the means of total capsulectomy.The authors will discuss the preliminary result of 2.5 years follow-up of this study.
- Signal Transduction Related Oncogenes in Human Adrenal Cortical Tumor; Gsα Giα, CREB.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Sung Kil Lim, eun Kyung Jung, Hyung Chun Park, Woo Hee Jung, Dong Whan Shin, Hyun Suk Lee, Yung Dae Yoon
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):350-357. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Functioning adrenal cortical tumors are originated form a distinct zone(zonna glomerulosa, zonna fasciculata or zonna reticularis) or the transitonal zone of adrenal gland. Each zone of the gland is regulated by their specific hormons or cytokines, and their signal transduction systems are different. The oncogenes of many endocrine tumors were mutated proteins involved in signal transduction, however gip is the only reported oncogene in adrenal cortical tumors. Therefore we decided to reevaluate whether gsp might be detected as an oncogene in several different functioning adrenal tumors, and we also tested whether CREB protein is a tentative oncogene or not. In our study, gsp was not detected in 13 patients, however gip was not also detected unexpectedly. There were no mutations in the phosporylation site of CREB("P" box) in adrenal cushing syndrome. We concluded that gip was not a oncogene detected frequently in adrenal cortical tumor, and CREB protein was not considered as a tentative oncogen, because there might be no amplification of the signals due to its extreme distal component of PKA or PKC system.
- The Effect of Methimazole on the Thyroglobulin Synthesis in Cultured Porcine Thyroid Cells.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Kyung Rae Kim, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Mi Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):332-336. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The thioureylene drugs, propylthiouracil and methylmercaptoimidazol(MMI), exert their antithyroid effect primarily through inhibition of thyroid peroxidase-catalyzed iodination of thyroglobulin. Recently the interest about the effect to the thyroglobulin synthesis of these drugs have been increasing. So we studied the MMI effect to the thyroglobulin synthesis in cultured porcine thyroid cells. Porcine thyroid cells were isolated by sequential trypsinization in the presence of EGTA, seeded at high density(1X10^6 cells/cm^2) and cultured. One week later, MMI was added in different concentrations(0, 0.2, 1, 5mM) with TSH only or with 4H(b-TSH, Insulin, Transferrin, Hydrocortisone) or without hormone. Medias were collected after 24 hours and compared the amount of thyroglobulin secreted. And also pulse-labeling were performed with S^35 cysteine/methionine(1-2uCi/well) for 30, 60, 90min at the same conditions.There was no significant change in the amount of the secreted thyroglobulin by MMI, and there was no significant change in the pulse-labeled interacellular thyroglobulin by MMI. And also there was no significant change in the secretion of TSH-stimulated thyroglobulin by MMI. So we conclude that MMI has no effect on the thyroglobulin synthesis in cultured porcine thyroid cells and also MMI has no effect on the TSH-stimulated thyroglobulin synthesis in cultured porcine thyroid cell.
- The Effect of Iodine on the thyroglobulin Synthesis in Cultured Porcine Thyroid Cells.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Kyung Rae Kim, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Mi Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):318-324. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The amount of thyroglobulin synthesized from thyroid cells and stored in colloid space in very important in thyroid hormone synthesis. The thyroglobulin synthesis is mainly regulated by TSH secreted from the pituitary gland. But recently there were some reports about the possibility that iodine regulated the thyroid protein synthesis. So our studied were conducted to determined whether iodine could have inhibitory effect on thyroglobulin synthesis and methimazole could abolish the inhibitory effect of idoine.Porcine thyroid cells were isolated by sequential trypsinization in the presence of EGTA, seeded at high density(1X10^6 cells/cm^2) and cultured. One week later, Nal was added in different concentrations(10^-7, 10^-6, 10^-5, 10^-4M). 24hour medias were collected and checked the amount of thyroglobulin secreted. And also pulse-labeling were performed with[^35S] cysteine/methionine(1-2 uCi/well) for 1 hour at the same conditions. We used 3mM methimazole and 10^-4M NaI to observe the blocking effect of methimazol in iodine.The extracellular thyroglobulin secretion was significantly decreased by iodine in dose dependent manner(82.4%, 80.7%, 76.8% and 73.1% of control). And also intracellular thyroglobulin synthesis was significantly decreased by iodide in dose dependent manner(100.5%, 83.4%, 82.3% and 79.4% of control). The inhibitory effect of iodide was abolished by methimazole(74.7% to 101.3% of control). These data indicate that high iodide inhibit the thyroglobulin synthesis and secretion from the thyroid cells, and furthermore autoregulation by iodide may include thyroglobulin synthesis. And also this effect is dependent on the generation of an organic form of iodine because methimazole abolish the inhibitory effect of iodide.
- G Protein Oneogenes in Aeromegaly.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Hyun Chul Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(3):157-162. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Seasonal Variation in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in The Elderly in Korean.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Young Duk Song, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Kil Lim, Yoon Sok Chung
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(2):121-127. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The seasonal variations in the parameters of calcium metabolism including 25-hydroxyvitamin D were analyzed in 19 free-living elderly subjects (mean age:68.7±6.7 yr) in Seoul. Mean serum total calcium concentration was 9.0±0.3 mg/dl in March and had risen to 9.3±0.3mg/dl in the following September(p<0.001). Despite their comparable calcium intake. Serum phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase concentrations did not show any seasonal variations, whereas serum PTH concentrations were significantly lower in September than in March(20.1±8.6 vs. 32.5±8.4 pg/ml, p<0.001). Seasonal changes in serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations were also found between the value(17.3±6.9 ng/ml) in March and that (28.5±7.4 ng/ml) in September(p<0.001). There was a significant correlation between seasonal increase in 25-hydroxyvitamin D and seasonal reduction in serum PTH/Cr(r=-0.5394, p<0.05). This study suggests that the winter minimum of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and the elevated PTH may be a contributing risk factor for the development of osteopenia especially in the elderly individuals. When exposure to sunlight is reduced, as in the case of nursing home population, an additional exogenous form of the vitamin D may be advisable.
- In Situ Hybridization Analysis of Human Growth Hormone and Prolactin Secreting Pitultary Adenomas.
-
Jae Wha Jo, Eun Jig Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Kyung Rae Kim, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Tae Seung Kim, Sun Ho Kim, Joong Uhn Choi, Kyu Chang Lee, Hyun Joo Jung, Sang Seop Chung
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(2):82-92. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A non-isotopic in situ hybridization method with biotin-labelled oligonucleotide probes was used to examine growth hormone(GH) and prolactin(PRL) gene expression in 32 patients with pituitary adenomas; 13 were prolactinomas, 8 GH secreting adenomas, and 11 mixed GH and PRL secreting adenomas.Positive immunostaining for GH was found in all patients with GH secreting adenomas, and mixed GH and PRL secreting adenomas. Positive immunostaining for PRL was found in all patients with prolactinomas and 9(81.8%) of 11 mixed GH and PRL secreting adenomas, 5(62.5%) of 8 GH secreting adenomas. Immunohistochemistry revealed that 13 were lactotrope adenomas, 5 somatotrope adenomas, and 14 GH and PRL cell adenomas.In situ hybridization revealed that GH mRNA expression was found in all the patients with somatotrope adenomas and GH and PRL cell adenomas, and 6(46.1%) of 13 lactotrope adenomas. PRL mRNA expression was 100% in lactotrope and GH and PRL cell adenomas, and 4(80.0%) of 5 somatotrope adenomas.The patients with a clinical diagnosis of acromegaly had detectable PRL mRNA in their neoplasm and it is suggested that the PRL cells in the adenomas did not result from dedifferentiation, but from the neoplastic stimulus for some mixed tumors probably occurred in cells previously committed to produce PRL and GH. In lactotrope adenomas, the PRL cells of the patients without expression of GH mRNA may be arised from cells programmed to secrete PRL or precussor PRL cells rather than from mixed GH-PRL cells. The finding that some patients produced mRNA detectable by in situ hybridization, but no hormone detectable by immunohistochemistry within tumor was suggested of a silent adenoma.These observations indicated that in situ hybridization studies may improve the classification of pituitary adenomas and may provide a precise knowledge of the biology of these neoplasms.
- The effects of different hormone conditions on the structure of the thyroglobulin from cultured pig thyroid cells.
-
Kyung Rae Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(3):310-317. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Thyroglobulin synthesis in cultured porcine thyroid cells.
-
Kyung Rae Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Kyoung Mi Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(3):303-309. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against FRTL-5 cells in korean postpartum thyroiditis.
-
Hyun Chul Lee, Kwan Woo Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Kwang Jin Ahn, Jai Hee Jung, Yun Sok Chung, Mi Rin Kim, Hyeon Man Kim, Sung Kil Lim, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(3):296-302. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- A clinical study of cushing's disease.
-
Chan Hee Lee, Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Kyeong Mi Lee, Jae Sik Cho, Hyun Chul Lee, Dong Ik Kim, Doe Heum Yoon, Young Soo Kim, Sang Seop Chung, Kyu Chang Lee, Tae Seung Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(3):273-280. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Growth hormone response to L-dopa and pyridostigmine in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
-
Kyeong Mi Lee, Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Byung Seok Lee, Ki Hyun Park, Hee Dong Bae, Yoon Sok Chung, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(3):265-272. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- The effect of ipriflavone on postmenopausal osteoporosis.
-
Young Joon Weon, Yoon Sok Chung, Ki Young Hong, Yoo Kyoung Park, Hee Son Kim, Jong Ho Lee, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(3):259-264. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- The effect of body fat on bone density in pre-and postmenopausal women.
-
Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Yoon Sok Chung, Seog Won Park, Choon Hee Chung, Kwang Jin Ahn, Eun Jig Lee, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Mi Sook Choi, In Kyung Paik, Jong Ho Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(3):251-258. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- A case of cushing's syndrome due to bilateral macronodular adrenocortical hyperplasia associated with empty sella syndrome.
-
Jin Ahn Kim, Kyung Mi Lee, Yoon Sok Chung, Eun Tack Shin, Uk Hee Won, Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Ki Whang Kim, Hee De Lee, Woo Hee Jung
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(2):203-210. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- The correlation between body composition and bone mineral density in pre-and postmenopausal women.
-
Moon Suk Nam, Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Kyung Mi Lee, Yoon Sok Chung, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung Suk Lee, Ki Hyun Park, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(2):180-186. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Comparision of bone mineral density in acromegalic pateints according to the gonadal status.
-
Seog Won Park, Young Soo Kim, Woon Sok Chung, Kyung Mi Lee, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(2):149-156. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- alpha-subunit secretion of pituitary adenomas.
-
Kyeong Mi Lee, Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Yoon Sok Chung, Byoung Kwon Lee, Seg Won Park, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Doe Heum Yoon, Young Soo Kim, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(2):127-133. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- A case of pituitary metastasis from periampullary carcinoma.
-
Eun Tack Shin, Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Kyung Mi Lee, Hee Dong Bae, Kwan Sik Lee, Yoon Sok Chung, Kwang Jin Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(1):88-93. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Hereditary influence in determinig peak bone mass.
-
Ki Young Hong, Yoon Sok Chung, Sung Kil Lim, Young Duk Song, Moon Jeong Shim, Yoo Kyung Park, Jong Ho Lee, Hyun Yong Song, Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Soo Jae Moon
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(1):66-71. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone(GnRH) therapy in male patients with hypothalamic hypogonadism.
-
Seog Won Park, Yoon Sok Chung, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Eun Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Hyung Ki Choi, Moo Sang Lee, Ki Hyun Park
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1993;8(1):27-34. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Thyrotropin secreating pituitary adenoma.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyeon Man Kim, Yoon Sok Chung, Kwang Jin Ahn, Kyung Mi Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Duk Hi Kim, Dong Ik Kim, Doe Heum Yoon, Yong Gu Park
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1992;7(4):331-342. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Estrogen receptors of human pituitary adenomas.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Yoon Sok Chung, Kwang Jin Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Mi Rim Kim, Chang Mi Kim, Kyung Za Ryu, Do Heum Yoon, Sang Seop Chung, Kyu Chang Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1992;7(3):208-215. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Empty sella syndrome associated with diabetes insipidus: report of two cases.
-
Jae Hee Chung, Eun Jig Lee, Yoon Seog Chung, Eui Suk Whang, Kwang Jin Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1992;7(1):66-70. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Pituitary oncocytoma.
-
Eun Jig Lee, Kyung Rai Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kwang Jin Ahn, Yoon Sok Chung, Sung Kil Lim, Kap Bum Huh, Woo Ick Yang, Woo Hee Chung, Tae Seung Kim, Do Heum Yoon, Sang Seop Chung
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1992;7(1):16-23. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Clinical review of pheochromocytoma.
-
Shin Kee Ahn, Kwang Jin Ahn, Eun Jig Lee, Yoon Sok Chung, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Cheong Soo Park, Jin Moo Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1991;6(3):245-253. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
|